Fundamentals Of Anatomy, Physiology & Kinesiology: 11th Class – Chapter 8
Anatomy
- Anatomy is the scientific study of the structure of organisms including their systems, organs and tissues for example, the study of structure of heart is known as Anatomy of heart.
Physiology
- The working of all the systems of human body and their mutual relationship are studied. For example, the functioning of heart is known as Physiology of heart.
Kinesiology
- The word derived from the Greek work Kinesi which means motion and Logy means study.
- Kinesiology is the study of human or non-human body movement and their roles in promoting health and reducing disease.
Importance Of Anatomy & Physiology
- The knowledge of structure of organs: We get the knowledge of structure, shape, size, location & weight of all the systems of body for example, length of the bones & percentage of white / red fibers.
- The knowledge of functions of organs: Through the physiology, we get to know the function of nervous, excretory & circulatory systems for example, capacities of cardiovascular system.
- Prevention of injuries: Through the complete knowledge of anatomy & physiology, the sports person will prevent themselves from various injuries during sports training and competition.
- Helpful in process of Rehabilitation: The process of helping a person who has suffered as illness or injury to restore lost skill and regain maximum self sufficiency.
- Helpful in providing first aid: Due to sports injuries, a first aider should have the knowledge of the human anatomy & physiology only then first aid can be provided to the wounded persons.
- Techniques and skills: While teaching different techniques & skills the structure and function of various systems are studied in detail.
- Helpful in the preparation of Training programs: Good training programs can only be prepared if coaches basic knowledge of physiological capacities or limits of every sports persons.
- Evaluation of capacity of athlete: It can be done with the knowledge anatomy of physiology, to judge the vital capacity of respiratory system.
Importance Of Kinesiology
- Improved performance: As kinesiology deals with study of analyzing movements which helps in improving sports performance as it helps in correcting the movement.
- Safety: Kinesiology helps in designing movement experiences that avoid injuries and it also helps in designing safety equipment.
- Helps in developing motor skills: It helps in developing the motor skills and specialized sports skills that helps in better sports performance.
- Rehabilitation: After a injury a person requires to perform correct therapeutic exercises which are developed through the knowledge of kinesiology and it helps the ailing muscles.

Skeletal System
- It supports and protects the body.
- This system is composed of connective tissues including bone, cartilage, tendons and ligaments.
Joint
- A joint is the connection made between bones in the body which link the skeletal system into a functional whole.
Functions Of Bones
- Support: Bones a given support and stability to the whole body.
- Protection: Bones protect some soft and delicate organs of our body e.g. brain is protected by skull and the heart is protected by ribs.
- Giving shape to the body: Bones give shape to the body. A person’s height depends on bones.
- Movement: Bodily movement is carried out by the interaction of the muscular & skeletal system. The bones act as levers to make body possible to move.
- Formation of RBC: RBC’s build in the marrow of bones an average of 2.6 million.
- Storage of minerals: There are such bones that provide minerals such as calcium & phosphorus to the body which is very useful.
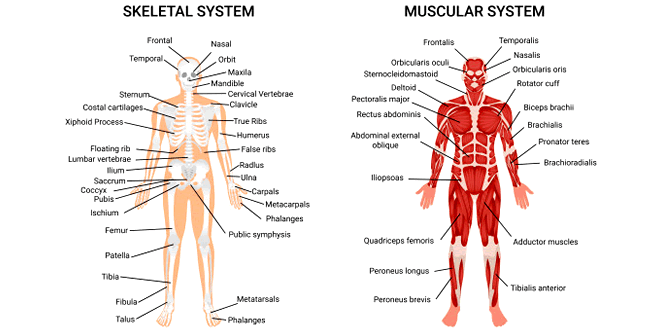
Classification Of Skeletal System
Long Bones
- These work as long as wide and they work as levers.
- These are situated in upper and lower limbs as shoulders, hands, hips and legs.
- Femur is the longest bone in the body.
Short Bones
- The bones are short and cubed shaped.
- These are found in wrist and ankle.
Flat Bones
- Flat bones have broad surfaces that protect the organs.
- These are found in upper limbs as skull & ribs.
Irregular Bones
- These bones have some special shape.
- They are 26 irregular bones which are found in spines.
Classification Of Joints: Fundamentals Of Anatomy, Physiology & Kinesiology
Immovable Joints
- These are also known as fixed joints because they are joined together through tissues and
- No movement is possible
- They are found in skull and face.
Slightly Movable Joints
- In these bones, the surfaces of bones are separated by some intervening substances.
- Only slightly movement is possible.
- They are found in spine and also known as cartilaginous joints because they are joined by cartilage.
Freely Movement Joints
They are also known as synovial joints because each contains synovial fluid which helps in decreasing friction among joining of bones and they can move to a greater extent.
- Ball and socket joint: These joints are formed in which the rounded head of one bone fits into the hollow of cup-shaped socket of another bone such as Shoulder and Hip joint.
- Gliding joint: It allows for gliding movements between flat surfaces as the surfaces slide over one another and the movement depends on the ligaments such as joints of wrist (Carpal Bones) & the ankle (Tarsal Bones).
- Hinge joint: In hinge joint one end of the joining bone is concave and the other is convex shaped. They joined in a way that the movement is possible in one plane. It is found in elbow joint.
- Pivot joint: The movement is restricted to rotational only and one bones turns around on another bone. It is found in neck.
- Condyloid joint: It is similar to hinge joint but it moves in two planes. It is found in wrist.
- Saddle joint: The joining bones of this types of joint has opposing ends as concavo-convex that permit movements in all directions except axial rotation. It is found in thumb.
Properties Of Muscles
All muscle cells share several properties:
Contractility
- The quality or capability of muscles to forcefully shrinking or shorten.
- Muscles carry out one highly specialized function that is known as contraction.
- Actin and myosin filaments are structure to produce muscular contraction.
Excitability
- The property of a muscle fiber is excitability that enables the muscles to respond to any kind of stimulation.
- The ability of a nerve or muscle cell to react to an electric stimulus is known as muscular excitability.
Extensibility
- It is the ability of the muscle to stretch maximally without tearing from normal resting length and beyond to a limited degree.
Elasticity
- It means that if muscles are extended, they shrink to their original resting length.
- The ability of a nerve or muscle cell to react to an electric stimulus is known as muscular excitability.
Functions Of Muscles: Fundamentals Of Anatomy, Physiology & Kinesiology
- Skeletal Muscles Create Movement: For all the larger of smaller movements, the central nervous system directs the muscles to contract and relax according to the need of the situation.
- Maintains Good Posture: To keep the body in correct posture the muscles are attached with the bones through ligaments and tendons which also maintains the balance and coordination of the body.
- Pumps Heart: Cardiac muscles are responsible for pumping the blood from the heart into the bungs to pick up oxygen, receiving blood back from the lungs and then pumping it to the various arteries of the body.
- Process Of Inhalation & Exhalation: The whole respiration process depends on inhalation and exhalation which is done by intercostal muscles through this oxygen is provided to the body.
- Helps In Digestion: Smooth muscles of organs like stomach and intestine help the digestive system in the process of digestion of food.
- Heat Generation: It is very important in cold climates. Due to high metabolic rate muscles produce great amount of heat in the body.
- Protect Organs & Bones: It protects the bones & organs by absorbing shocks and reducing friction in the joints such as muscles in the torso protect the internal organs at the front, sides, and back of the body.
Structure Of Muscles
Smooth, Non-Striated Muscles
This type of muscle is innervated from autonomic nervous system and generally contracts involuntarily. They are generally found in the walls of digestive tract, trachea, bronchus etc.
Cardiac Muscles
It is found only in heart. Cardiac muscle works just like striated muscle fiber. It contracts rhythmically and automatically wherever striated muscle can contract voluntarily.
Striated Skeletal Muscles
The fibers of skeletal muscle are cylindrical in shape. These muscles fibers have alternate light and dark bands.
Fundamentals Of Anatomy, Physiology & Kinesiology in Sports: Questions Carrying 03 Marks
- What is the importance of Anatomy and Physiology?
- Write any three functions of skeletal system.
- Explain the classification of skeletal system.
- Given mechanism of muscular contraction.
- Explain any two properties of muscles.
- Describe the process of breathing.
- Explain the circulation of blood.
- Explain static equilibrium.
- What do you mean by dynamic equilibrium?
Fundamentals Of Anatomy, Physiology & Kinesiology in Sports: Question Carrying 05 Marks
- Define Anatomy and Physiology. Explain its importance.
- Explain the various types of joints of human body.
- Describe the functions of muscles.
- Describe the structure of muscular system.
- Write about the structure of respiratory system.
- What are the functions of respiratory system?
- Explain the functions of circulatory system.
- Explain the application of equilibrium on sports.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students