Getting to Know Plants – 6th Class NCERT CBSE Science Chapter 07
Question: Correct the following statements and rewrite them in your notebook.
- Stem absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
- Leaves hold the plant upright.
- Roots conduct water to the leaves.
- The number of sepals and petals in a flower is always equal.
- If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are also joined together,
- If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is joined to the petal.
Answer:
- Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
- Roots hold the plant upright.
- Stem conducts water to the leaves.
- The number of petals and sepals in a flower is usually equal.
- If the sepals of a flower are joined together, its petals are not necessarily joined together.
- If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is not necessarily joined to the petal.
Question: Can you find a plant in your house or in your neighborhood which has a long but a weak stem? Write its name. In which category would you classify it?
Answer: Yes, we find a money plant in our house. It is a climber.
Getting to Know Plants – NCERT Question: What is the function of a stem in a plant?
Answer: A stem performs following functions:
- The stem and its branches hold leaves to get maximum sunlight.
- It transports water from roots to different parts of the plant.
- It transports food from leaves to different parts of the plant.
- It bears leaves, flowers and fruits.
Question: Which of the following leaves have reticulate venation?
Wheat, tulsi, maize, grass, coriander (dhania), china rose.
Answer: Tulsi, china rose.
Question: If a plant has fibrous root, what type of venation are its leaves likely to have?
Answer: Parallel venation.
Question: If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, what kind of roots will it have?
Ans: Tap root.
Question: Is it possible for you to recognize the leaves without seeing them? How?
Answer: We cannot exactly recognize the leaves without seeing them. We may be able to have some idea by touching and smelling them.
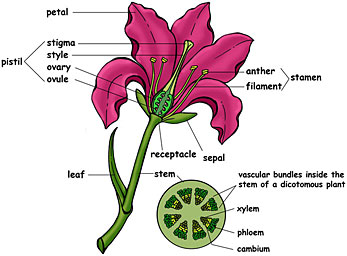
Question: Write the names of the parts of a flower in sequence, from outside to inside.
Answer: The names of various parts of a flower from outside to inside are:
- Sepals
- Petals
- Stamens
- Pistil
Question: Name the part of the plant which produces its food. Name this process.
Answer: Leaves produce food for the plant. This process is called photosynthesis.
Question: In which part of a flower you are likely to find the ovary?
Answer: We find ovary in pistil. It is the lowermost part of the pistil.
Question: Name two flowers, each with joined and separates sepals.
Answer:
- Flowers with joined sepals:
(i) Datura
(ii) Loki - Flowers with separate sepals:
(i) Gurhal
(ii) Mustard
Getting to Know Plants – NCERT Question: List few plants found around your house.
Answer: Mango, neem, grass, chilli, palak and banyan tree.
Question: Are all the plants same in size?
Answer: No, all plants are of different sizes.
Question: What are the major parts of plants?
Answer: Stem, root, leaves and flowers.
Getting to Know Plants – NCERT Question: How many kinds of plants are there?
Answer: There are three kinds of plants:
- Herbs
- Shrubs
- Trees
Question: Name two plants that belong to herbs.
Answer:
- Tomato
- Potato
Question: Give two examples of shrubs.
Answer:
(i) Lemon
(ii) Orange
Question: Give two examples of trees.
Answer:
- Mango
- Neem
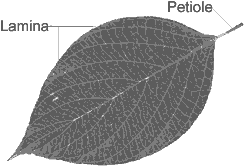
Question: Define petiole.
Answer: The part (stalk) of a leaf by which it is attached to the stem is called petiole.
Question: What is lamina?
Ans: The broad green flat part of leaf is called lamina.
Question: What are veins?
Answer: The lines on the leaf are called veins.
Getting to Know Plants – NCERT Question: What is midrib?
Answer: A thick vein in the middle of the leaf is called midrib.
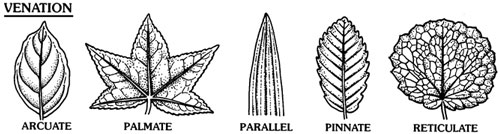
Question: What do you mean by leaf venation? Explain various types of leaf venation with example.
Answer: Leaf venation: The design made by veins in a leaf is called leaf venation. There are the following two types of leaf venation:
- Reticulate venation: If the design of veins makes a net-like structure on both the sides of midrib then it is called Reticulate venation. For example, mango leaf, gram leaf.
- Parallel venation: If the veins are parallel to each other or to midrib then such type of venation is called parallel venation. For example, wheat leaf, barley leaf.
Question: What is transpiration?
Answer: The process by which water comes out from the leaves in the form of vapour is called transpiration.
Question: Name the process by which leaves can prepare their food.
Answer: This process is called photosynthesis.
Question: What are the raw materials for photosynthesis?
Answer:
- Sunlight
- Water
- Carbon dioxide
- Chlorophyll
Question: Where does the photosynthesis take place in plants?
Answer: It takes place in the leaves.
Question: Name the part of plant which helps in holding the plant in the soil.
Answer: Roots.
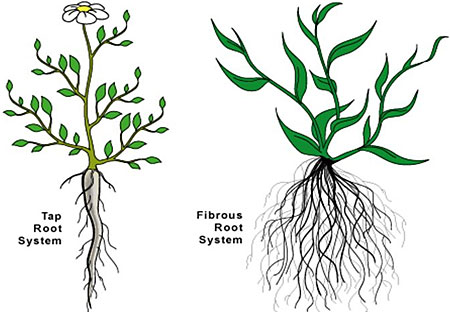
Getting to Know Plants – NCERT Question: What are tap roots?
Answer: The roots in which one root is main root and other lateral roots grow on it are called tap roots.
Question: Give names of two plants which have tap root.
Answer: Gram and mustard.
Question: Name two plants which have fibrous root.
Answer:
- Wheat plant
- Maize plant
Question: What are lateral roots?
Answer: The smaller roots that grow on the main tap root are called lateral roots.
Question: What are fibrous roots?
Answer: The roots which do not have any main root but all the roots are similar are called fibrous root.
Question: Does the stem prepare food for any plant?
Answer: Yes, there are some plants whose stem prepares food, e.g. cactus.
Question: Name the prominent parts of a flower.
Answer: The prominent parts of a flower are petals, sepals, stamens and pistil.
Question: What are sepals? What are their functions?
Answer: The small green colored leaf-life structures are called sepals. It protects flower when it is in stage of bud.
Question: What are petals? Why are they generally colored?
Answer: The colored big leaf-life structures present in flower are called petals. Petals are colored so as to attract insects for pollination.
Question: What are stamens?
Answer: When we remove sepals and petals from the flower then we see some filaments in the flower which are called stamens. These, are the male part of the flower.
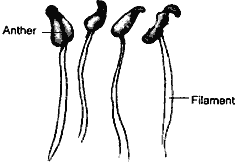
Question: Name various parts of stamen.
Answer: There are two parts of a stamen:
- Anther
- Filament.
These are the male part of the flowers.
Question: Name the various parts of pistil.
Answer: There are three parts of pistil:
- Stigma
- Style
- Ovary
Question: What are ovules?
Answer: These are small bead-like structures inside the ovary.
Question: What are weeds?
Answer: The unwanted plants that grow in the fields with the main crops or in their surroundings are called weeds. Weeds are the plants which are not grown by the farmers. For example: grass.
Question: Classify plants and give an example of each.
Answer: On the basis of various characteristics most of the plants can be classified into three categories:
- Herbs, e.g. tomato
- Shrubs, e.g. lemon
- Trees, e.g. mango
Question: What are herbs? Give two examples.
Answer: The plants with green and tender stems are called herbs. They are usually short and may have no or less branches. For example, tomato, potato.
Question: What are shrubs? Give two examples.
Answer: The plants which have a hard but not a very thick stem are called shrubs. Such plants have the stem branching out near the base. For example, lemon, rose plants.
Question: What are trees? Give two examples.
Answer: The plants which are very tall and have hard and thick brown stem are called trees. The stems have branches in upper part and much above the ground. For example, mango, neem.
Question: What are creepers? Write an example.
Answer: The plants with weak stem that cannot stand upright and spread on the ground are called creepers. Various types of grasses are the examples of creepers.
Question: What are climbers?
Answer: The plants that take support of neighbouring structures and climb up are called climbers. They have weak stem. For example, grapes, money plant, beans.
Question: Explain an activity to show that stem conducts water and other substances.
Answer: Take some water in a glass. Add few drops of red ink to the water. Cut the stem of a herb plant from its base. Put it in the glass as shown in figure. We will see that some parts of the stem become red. This activity shows that stem conducts water.
Question: Explain the structure of a leaf with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer: There are two main parts of leaf:
- Petiole: The part of the leaf by which it is attached to the stem is called petiole.
- Lamina: The broad, green part of the leaf is called lamina.
The lamina contains following parts:
- Veins: There are various types of lines on the leaf. These lines are called veins.
- Midrib: There is a thick vein in the middle of the leaf. This vein is called midrib.
Question: Explain the main functions of leaf.
Answer: There are following two main functions of leaf:
(i) Transpiration: The extra water comes out of the leaves in the form of vapour. This process is called transpiration.
(ii) Photosynthesis: The process by which leaves prepare their food from water and carbon dioxide, in the presence of sunlight and a green-coloured substance, is called photosynthesis.
Question: What are unisexual and bisexual flowers?
Answer:
- Unisexual flower has either male (stamen) or female (pistil) parts.
- Bisexual flowers have both male and female whorl in the flowers, i.e., they have both stamen and pistil.
Question: Name a plant that eats insect.
Answer: Pitcher plant
Question: Pitcher plant has green leaves which can prepare food by photosynthesis then why does it eat insects?
Answer: To get nitrogenous compounds which it cannot absorb from the soil.
Question: Name a plant that has underground as well as aerial (above the ground) root system.
Answer: Banyan tree.
Question: Why do we see dew drops on leaves in the early morning?
Answer: At night the water lost by leaves does not get evaporated and gets collected on the leaves in the form of dew drops.
Getting to Know Plants – NCERT Question: Why are petals colorful?
Answer: The colorful petals attract insects for pollination.
Question: Why does white flowers bloom at night?
Answer: White colour attracts night insects for pollination.
Question: What do you mean by a complete and incomplete flower?
Answer: The flower with all whorls, i.e., sepals, petals, stamen and carpel in it is a complete flower. If any one of this is absent in a flower it is called an incomplete flower.
Question: Leaves need oxygen and carbon-dioxide (for photosynthesis). How do they get these gases?
Answer: Leaves take in these gases from atmosphere through small pores present on them called stomata.
Question: How can one de-starch the leaves of potted plant without plucking, them?
Answer: By keeping it in dark for 2-3 days.
Question: What is the relation between leaf venation and the type of roots?
Answer: The plants having tap root have reticulate venation. The plants having fibrous roots have parallel venation.
Question: Differentiate between tap root and fibrous root.
Answer:
Tap root goes deep into the soil.
Tap roots are found in plants which have reticulate venation in their leaves.
They do not go deep into the soil.
These are found in plants which have parallel venation in their leaves.
Question: Describe the structure of a typical flowers with a well-labeled diagram.
Answer: A typical flower contains the following parts:
- Stalk: The part by which a flower is attached to the branch is called stalk.
- Sepals: The small green leaf-like structures of the flower.
- Petals: The big colored leaf like structure are called petals to attract pollinators.
- Stamen: It is the mole part of a flowers.
- Pistil: The inner most part of a plant. It contains with (a) Stigma, Style and ovary. (b) It is the female parts of a plant.
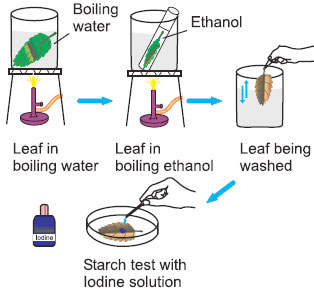
Question: Explain an activity to test the presence of starch in a leaf.
Answer: Take a leaf in a test tube and pour spirit till it completely covers the leaf. Now put the test tube in a beaker having water. Heat the beaker till all the green colour from the leaf comes out into the spirit in the test tube. Take out the leaf and wash it with water. Put it on a plate and pour some iodine solution over it. The iodine solution is brown in colour but when it comes in contact with starch it turns blue-black. The iodine solution will turn blue-black when dropped on the leaf, this confirms the presence of starch in the leaf.
Question: Explain that sunlight is essential for photosynthesis.
Answer: Take a potted plant having green leaves. Place it in a dark room for a day or two so that all the starch present in leaves is used by the plant. Now cover a portion of leaf with black paper and keep the plant in the sun for a day. Pluck the leaf, remove the black paper and test it for the starch. We see that only that part of the leaf becomes blue-black which was open to sun. The covered part does not become blue-black. This shows that no starch is formed because it gets no sunlight.
Getting to Know Plants – NCERT Question: Explain the important functions of root.
Answer: The following are the functions of root:
- They help to absorb water from the soil.
- The roots help in holding the plants firmly in the soil.
- They are said to anchor the plant to the soil.
Question: Explain various kinds of roots with the help of an example.
Answer: There are following two types of roots:
- Tap roots: The roots which have one main root and other smaller lateral roots are called tap roots. For example, mustard plant, gram.
- Fibrous roots: The roots which have no main root but all the roots appear similar are called fibrous roots. For example, maize, wheat.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students