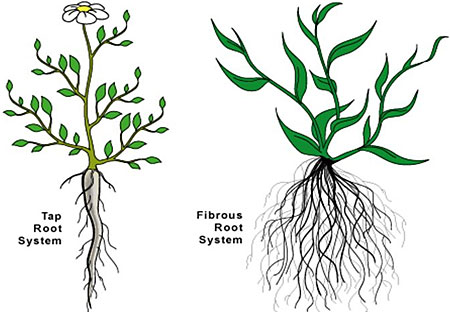
Question: Differentiate between tap roots and fibrous roots?
Answer: Tap Roots:
- It has 1 main primary root which arises from the base of the stem other roots are called secondary root.
- It can go very deep.
- It is stronger than (monocot) fibrous root.
- It is founded in dicot plants.
Fibrous roots:
- Many small like roots that arise from the base of the stem.
- It cannot go that deep.
- It is not that stronger like tap roots.
- It is found in monocot plants.
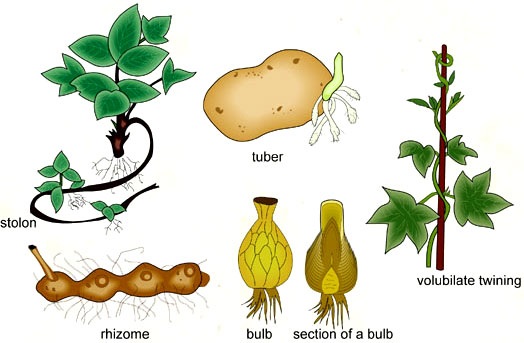
Question: Briefly explain various roots modifications.
Answer:
- Sliet Roots: to give extra supper to thin and long stem so that it can storm erect. Eg- lamboo, sugarcane.
- Prop roots: roots that reach the ground and fix themselves in the soil and give support to spreading branches.
- Roots for support: money plant to help in attaching the weak stem to support.
- Breathing roots: man grooves help the roots to breath in marshy are.
- Staring roots: carrot, Radish, turnip, store food for the plant.
Question: Briefly explain various stem modification.
Answer:
- Storing food: Some plants like potato, onion, garlic and sugarcane Store food in their stems.
- Photosynthesis: Cactus, young plants have chlorophyll which makes photosynthesis.
- Support: Tendrils, grape vine take support from any thing that they find nearby.
- Protection: Rose protects itself through its thorns present on its stems.
- Storing water: Cactus, baobab store water in their stems.
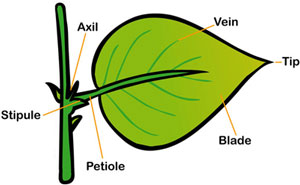
Question: Draw a well labelled diagram of a leaf with it functions.
Answer: Functions:
- It exchanges gases through stomata.
- Makes food by photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
- Transpiration (loss of water)
It is also known as food factory of the plant.
Question: What are the functions of the network of wins in a leaf?
Answer: The veins in a leaf transport water, minerals and food and they also provide support to the leaf.
Question: What is pollination?
Answer: Pollination occurs when pollen grains ferried from the an these to the stigma. After pollination, the ovary swells up to become a fruit and the ovules change into seeds.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students