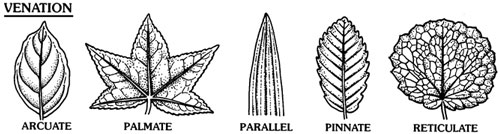
Question: What do you mean by leaf venation? Explain various types of leaf venation with example.
Answer: Leaf venation: The design made by veins in a leaf is called leaf venation. There are the following two types of leaf venation:
- Reticulate venation: If the design of veins makes a net-like structure on both the sides of midrib then it is called Reticulate venation. For example, mango leaf, gram leaf.
- Parallel venation: If the veins are parallel to each other or to midrib then such type of venation is called parallel venation. For example, wheat leaf, barley leaf.
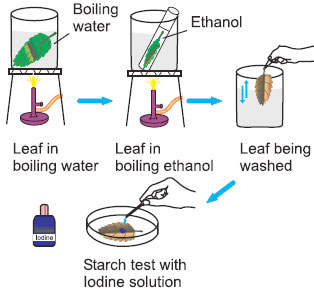
Question: Explain an activity to test the presence of starch in a leaf.
Answer: Take a leaf in a test tube and pour spirit till it completely covers the leaf. Now put the test tube in a beaker having water. Heat the beaker till all the green colour from the leaf comes out into the spirit in the test tube. Take out the leaf and wash it with water. Put it on a plate and pour some iodine solution over it. The iodine solution is brown in colour but when it comes in contact with starch it turns blue-black. The iodine solution will turn blue-black when dropped on the leaf, this confirms the presence of starch in the leaf.
Question: Explain that sunlight is essential for photosynthesis.
Answer: Take a potted plant having green leaves. Place it in a dark room for a day or two so that all the starch present in leaves is used by the plant. Now cover a portion of leaf with black paper and keep the plant in the sun for a day. Pluck the leaf, remove the black paper and test it for the starch. We see that only that part of the leaf becomes blue-black which was open to sun. The covered part does not become blue-black. This shows that no starch is formed because it gets no sunlight.
Question: Explain the important functions of root.
Answer: The following are the functions of root:
- They help to absorb water from the soil.
- The roots help in holding the plants firmly in the soil.
- They are said to anchor the plant to the soil.
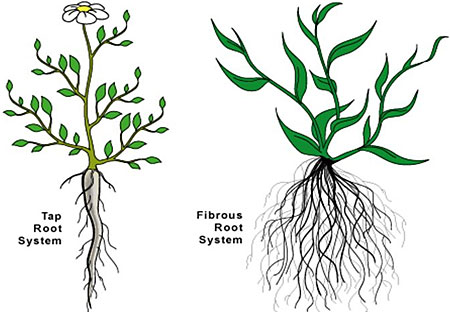
Question: Explain various kinds of roots with the help of an example.
Answer: There are following two types of roots:
- Tap roots: The roots which have one main root and other smaller lateral roots are called tap roots. For example, mustard plant, gram.
- Fibrous roots: The roots which have no main root but all the roots appear similar are called fibrous roots. For example, maize, wheat.
Question: List any two leaf modification with example.
Answer: The leaf modification are:
- Leaves of some plants are modified to from special structures called tendrils. Tendrils help plants to attach themselves to a support. For Eg: Pumpkin.
- For protection, leaves of certain plants get modified to from spines. Spines also reduce the amount of water lost from the plant. For Eg: Cactus.
Question: Define pollination? What happens to plant after pollination?
Answer: The transfer of pollen grains from another to a stigma is called pollination. Many flowers are brightly coloured and have a sweet smell to attract insects like bees. When the insect sits on the flower, the pollen grains stick to its body and may get rubbed off when it sits on another flower. This helps in pollination. After pollination, the ovules change into seeds. As seeds form, the overy develops into a fruit. Under suitable conditions availability of water, air and warmth, a seed become a baby plant.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students


