Question: Blue litmus paper is dipped in a solution. It remains blue. What is the nature of the solution? Explain.
Answer: If a blue litmus paper when dipped in a solution, remains blue, it implies the solution is either basic or neutral.
Question: What are salts? Are they acidic, basic or neutral? Give examples.
Answer: Salts are the ionic compounds generally formed by the neutralization of an acid with a base. They can be acidic, basic or neutral.
Examples of salts are:
(a) Acidic Salts: sodium bicarbonate
(b) Basic Salts: magnesium chloride
(c) Neutral Salts: Sodium chloride, potassium chloride
(d) Mixed Salts: bleaching powder, potash alum
Question: Distinguish between organic acids and mineral acids.
Answer: The difference is as follows:
Question: What are universal indicators and what are their uses?
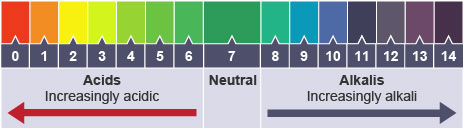
Answer: Universal indicators are compounds that show a gradual change in colour to indicate the acidity or basicity for pH values from 1-14. These colours indicate the basicity and acidity of a chemical. These indicators are available both as strip of paper called pH paper and as solution.
To find the pH value of unknown solution, the change in colour of these substances can be compared with that of the standard colour chart.
Question: Distinguish between strong and weak bases.
Answer: The difference is as follows:
Question: Ammonia is found in many household products, such as window cleaners. It turns red litmus blue. What is its nature?
Answer: Since it turns red litmus blue, Ammonia is basic in nature.
Question: Name the source from which litmus solution is obtained. What is the use of this solution?
Answer: Litmus is extracted from plant lichens. It has a mauve (purple) colour when dissolved in distilled water. Litmus solution is used to detect acidic or basic nature of any substance. When added to an acidic solution, it turns red and when added to a basic solution, it turns blue.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students



Such a nice app and I have learnt a lot of thing from it.