Air: NCERT 7th Class CBSE Social Science – Geography
Question: Define the term atmosphere.
Answer: Blanket of air surrounding the earth is known as the atmosphere.
Question: How do all living beings depend on the atmosphere for their survival?
Answer: All living beings depend on the atmosphere for their survival.
- Atmosphere provides them the air they breathe.
- It protects them from the harmful effects of the sun’s rays.
- Without its protection, they would be baked alive by the heat of the sun during day and get frozen during night.
Question: What is green house effect?
Answer: Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere traps the heat radiated from the earth creating a green house effect. This makes the temperatures livable. Without this earth would have been too cold to live. But the increased emissions from vehicles and factories increases the temperature leading to global warming.
Question: What is global warming? What is its affect?
Answer: When the heat retained through greenhouse gas increases the temperature of the earth, it causes global warming:
- The plants maintain the balance of gases. However this balance is upset by burning fuels such as coal, petroleum oil and large scale deforestation.
- This rise in temperature causes the snow in coldest parts to melt.
- As a result the sea level rises causing floods in the coastal areas.
- This may bring changes in weather and climate leading to extinction of certain plants and animal species.
Question: Name the two gases which influence the atmosphere to a great extent.
Answer:
- Two gases such as carbon dioxide and ozone influence the atmosphere to a large extent.
- Their percentage in the atmosphere is as under:
- Carbon dioxide 0.03%
- Ozone 0.00006%
Question: Describe the composition of the atmosphere.
Answer: Composition of the Atmosphere:
- The air we inhale while breathing is actually a mixture of numerous gases.
- Nitrogen and oxygen are two gases which make up the most of the atmosphere.
- Carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, argon and hydrogen are found in lesser quantities.
- Tiny dust particles are also present in the air.
Question: How is nitrogen present in atmosphere used by plants?
Answer: Nitrogen is the most plentiful gas in the air.
- Plants need nitrogen for their survival. They cannot take nitrogen directly from the air
- Bacteria in the soil or the roots fix nitrogen by changing its form so that plants can use it
Question: Which is the second most plentiful gas in the atmosphere?
Answer: Oxygen is the second most plentiful gas in the atmosphere. Humans and animals use it for breathing. Green plants produce oxygen through photosynthesis and thus oxygen balance is maintained in air. This gets disturbed if we cut trees.
Question: Explain how the oxygen and carbon dioxide balance is maintained in air?
Answer: Green plants use carbon dioxide to make their food and during this process release oxygen:
- Humans and animals release carbon dioxide and take oxygen from air
- The amount of carbon dioxide released by them is equal to amount used by plants to make their food. Hence a balance is maintained
- But now the excess of carbon dioxide is released by burning of fuels. The reduction in number of plants upset the balance of gases like carbon dioxide affecting earth’s weather and climate
Question: Explain the circulation of air in atmosphere.
Answer: When air is heated it expands, becomes lighter and rises up:
- Cold air is dense, so, it sinks down
- When hot air rises up, cold air from surrounding areas fills in the gap
- This is the process of circulation of air
Notes: News reports around the world
- Due to burning of fuels and cutting of trees CO2 level are increasing
- Globed sunscreen thinned
- Warning unstoppable
- It can bring back Jurassic era
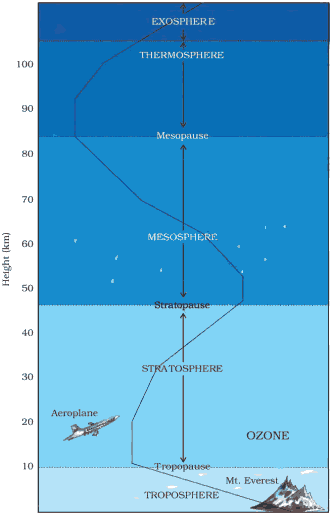
Structure of the Atmosphere
Question: Discuss the structure of the atmosphere.
Answer: Structure of the Atmosphere:
The atmosphere is divided into five layers according to height, starting from the earth’s surface.
They are
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
- Exosphere
Question: Which is most important layer of the atmosphere?
Answer: Troposphere
- Troposphere is the important layer of the atmosphere
- Its average height is 13 km
- It is 8 kilometers on the poles and 18 kilometers on the equator
- The air (which living beings breathe) exists here
- All the weather phenomena like winds, rainfall, fog, hailstorm etc. occur in this layer
Question: Which layer the most suitable conditions for flying airplanes?
Answer: Stratosphere:
- The stratosphere lies above the troposphere
- It extends up to a height of 50 km
- This layer is almost free from clouds
- No weather phenomenon occurs in this layer making conditions most ideal for flying airplanes
- Stratosphere contains a layer of ozone gas
- It protects living beings from the harmful effects of the sun rays
Question: What is the third layer of atmosphere?
Answer: Mesosphere:
- Mesosphere is the third layer of the atmosphere.
- It lies above the stratosphere.
- It extends up to a height of 80 km.
- Meteorites bum up in this layer on entering from the space.
Question: Briefly write about Thermosphere?
Answer: Thermosphere
- In Thermosphere temperature rises very rapidly with increasing height
- Ionosphere is a part of this layer
- It extends between 80 and 400 km
- This layer helps in radio transmission
- Radio waves transmitted from the earth are reflected back to the earth by this layer
Question: Which is the uppermost layer of the atmosphere?
Answer: Exosphere
- The uppermost layer of the atmosphere is known as exosphere
- This layer has very thin air
- Light gases like helium and hydrogen float into the space from here
Notes: Many questions are asked about days conditions especially on an important day like cricket match or wedding etc. Questions like – will it rain or will it be sunny; etc. basically are related to day’s weather. Such questions are not asked about climate
Question: What is weather?
Answer: Weather is the day to day condition of the atmosphere. For example a sunny day or rainy day. Weather is like a control knob of climate.
Question: Define the term climate.
Answer: The sum total of all weather conditions prevailing over large area for a longer period of time is called climate.
Question: What is the difference between weather and climate?
Answer: Weather is hour-hour conditions of atmosphere like hot humid weather may make us irritable but same day breezy or pleasant evening may make one cheerful. We have hot or cold climate over a period of few months.
Therefore we have daily forecast of weather and long term predictions of climatic conditions.
Question: Name different types of weather measuring instruments.
Answer:
- Thermometer – measures temperature
- Barometer – measures atmospheric pressure
- Rain Gauge – measures amount of rainfall
- Wind Vane – shows direction of wind
Question: What is temperature?
Answer:
- The degree of hotness or coldness is called the temperature
- Temperature changes not only between day and night but also from season to season
Question: What is Insolation?
Answer: Insolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth. It influences the distribution of temperature.
Question: Why are poles covered with snow?
Answer: The amount of Insolation decreases from equator towards poles, therefore the temperature also reduces. But if the earth’s temperature rises too high, it would be too warm to raise crops.
Question: Why cities are more hotter than villages?
Answer: The temperature in cities is much higher than that of villages because the concrete and metals in the buildings and the tar and asphalt in the roads gets heated throughout the day and absorbs heat. This heat is released at night hence there is the difference in the temperature.
The crowded high rise buildings trap the warm air and thus raise the temperature of the cities.
Question: Why don’t we feel the air pressure?
Answer: The air above us presses us from all sides with great force but we do not feel it. This happens because our body exerts a counter pressure.
Question: Define the term air pressure.
Answer: Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface. As we move in the upper layers of atmosphere, the pressure falls rapidly.
Question: How does air pressure vary from equator to poles and from surface to heights?
Answer: Variation in Distribution of Pressure
- As we go up the layers of atmosphere, the pressure falls rapidly
- The air pressure is highest at sea level
- It decreases with increase in height
- Horizontally the distribution of air pressure is influenced by temperature of air at a given place
Question: What is the relation between temperature and pressure?
Answer: Distribution of air pressure is influenced by the temperature of the area:
- Where temperature is high the air gets heated and rises. This creates a low pressure area.
- Low pressure is associated with cloudy skies and wet weather.
- In areas with low temperature, the air is cold and heavy so, it sinks down. This creates a high pressure area.
- High pressure is associated with clear and sunny skies.
- Air always moves from high pressure to low pressure areas.
Question: Why do Astronauts wear a protective gear on moon?
Answer: Astronauts wear a protective suit filled with air when they go to moon because the counter pressure exerted by the body would make the blood vessels burst.
Question: Define the term wind. Explain with examples.
Answer: The movement of air from high pressure to low pressure areas is called wind. For example wind blows dry leaves or strong wind uproots trees. Blowing smoke or dust is the work of wind. Strong wind makes it difficult to walk or hold umbrella.
Question: Which are the three components of cyclone?
Answer: Three components of cyclone are wind velocity, rain and tidal surge.
Question: What are the various categories of wind? Explain with a diagram.
Answer: Winds can be broadly divided into three types:
- Permanent winds: which blow constantly throughout the year in a particular direction.
Example, easterlies and westerlies. - Seasonal winds: which change directions in different seasons. For example, monsoon winds.
- Local winds: blow only during a particular period of the day or the year in a small area. For example, land or sea breeze or loo.
Question: What is cyclone?
Answer: A powerful and destructive storm with very high speed winds that moving in circular motion around an area of low pressure.
Question: Describe the fury of cyclone taking example of ‘Super cyclone’ of Odisha.
Answer: Odisha on eastern sea coast of India is prone to cyclones originating in Bay of Bengal.
- Odisha was hit by cyclone on 17th-18th October 1999 and again on 29th October.
- Cyclone originated as a ‘depression’ in the Gulf of Thailand near Port Blair.
- It moved in northwest direction on 25th October and intensified into super cyclone and hit Odisha.
- Wind speed was up to 260 km/hr which lasted for 36 hours.
- Trees were uprooted kutcha houses, roof tops industrial sheds etc blown away.
- Power supply and communication lines damaged.
- Continues rains flooded the major rivers. Tidal waves swept 20 km of inland areas including cities of Bhubaneshwar and Cuttack and destructed 28 coastal towns.
- 7-10 m high tidal waves caused damage to paddy crops, vegetables fruits and agricultural land turned infertile due to salinization.
- 13 million people were affected. Livestock was killed.
- Plantations of teak, sal, bamboo, mangrove forests of Paradeep and Konark disappeared.
Question: What is humidity?
Answer: When water evaporates from different water bodies and land it turns into water vapours or moisture. Moisture in air at any time is known as humidity.
Question: What is a humid day?
Answer: A day when air is full of water vapour is called a humid day. With the air getting warmer its capacity to hold moisture increases so it becomes more humid. On such days clothes takes longer to dry and even body sweat does not evaporate easily.
Question: How are clouds formed? How do clouds cause precipitation?
Answer:
- When water vapour rises, it starts cooling.
- Water vapour condenses which results in formation of droplets of water.
- These droplets hanging in the air above are called clouds.
- Clouds are masses of these water droplets.
- When these droplets of water become too heavy to float in the air, they come down as precipitation.
Question: Why do jet planes leaves a white trail behind them?
Answer: Jet planes flying in the sky leave a white trail behind them,
- The moisture from their engines condenses.
- We see trails of this condensed moisture for sometime when there is no air movement to disturb it.
- These trails of condensed moisture are actually clouds.
Question: What are different forms of precipitations?
Answer: Different forms of precipitations are: dew, rainfall, hail, snowfall, fog, sleet.
Question: What is rain? What is its importance?
Answer: Precipitation in liquid form is called rain. Most of the ground water comes from rainwater. It is important for survival of plants and animals. It brings fresh water to earth.
If rainfall is more or trees are cut on hills, rain water can cause flooding in low lying areas. If it is less than water scarcity or drought may occur.
Question: What are the types of rainfall?
Answer: Based on the mechanism rainfall can be of three types: Convectional, Orographic or Cyclonic.
Question: Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
- Earth is surrounded by a blanket of air called ………………..
- Green plants produce ……………………… during photosynthesis.
- Increased volume of ……………………. is affecting the earth’s weather and climate.
- Ionosphere is the part of ……………………….
- Amount of rainfall is measured by ………………………
- Insolation influences the distribution of ……………………
Answer:
- Atmosphere
- Oxygen
- Carbon dioxide
- Thermosphere
- Rain gauge
- Temperature
Question: State whether the given statements are true or false.
- Hot air is dense and heavy and cold air is lighter and expands.
- Without Green house effect earth would have been too cold to live.
- Ionosphere contains the ozone layer.
- Helium and hydrogen float from exosphere into space.
- Wind – vane shows the direction of wind.
- Air moves from high pressure to low pressure.
Answer:
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
Question: Answer the following questions briefly.
- What is atmosphere?
- Which two gases make the bulk of the atmosphere?
- Which gas creates greenhouse effect in the atmosphere?
- What is weather?
- Name three types of rainfall
- What is air pressure?
Answer:
(i) Atmosphere is a thin blanket of air that surrounds the earth. It protects us from the harmful rays of the sun. It consists of several gases in which nitrogen and oxygen occupy the major portion.
(ii) Nirtrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%) make the bulk of the atmosphere.
(iii) Carbon dioxide creates greenhouse effect in the atmosphere.
(iv) Weather is hour-to-hour, day-to-day condition of the atmosphere.
(v)
- Convectional rainfall
- Orographic rainfall
- Cyclonic rainfall.
(vi) The pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface is known as air pressure.
Question: Tick the correct answer:
- Which of the following gases protects us from harmful sun rays?
(a) Carbon dioxide (b) Nitrogen (c) Ozone - The most important layer of the atmosphere is
(a) Troposphere (b) Thermosphere (c) Mesosphere - Which of the following layers of the atmosphere is free from clouds?
(a) Troposphere (b) Stratosphere (c) Mesosphere - As we go up the layers of the atmosphere, the pressure
(a) Increases (b) Decreases (c) Remains the same - When precipitation comes down to the earth in the liquid form, it is called
(a) Cloud (b) Rain (c) Snow
Answer: (i)—(c), (ii)—(a), (iii)—(b), (iv)—(b), (v)—(b)
Question: Give reasons:
- Wet clothes take longer time to dry on a humid day
- Amount of Insolation decreases from equator towards poles?
Answer:
- On a humid day the air is full of water vapour. Hence, evaporation is very slow. This is the reason why wet clothes take longer time to dry on a humid day.
- Insolation comes through vertical rays on equator. Thus, it covers up less space but we feel more heat there when it goes up from equator towards poles, the sun rays become slanting. Needless to say that slanting rays come on the earth covering longer distance. Although these slanting rays heat up more space, the degree of hotness is felt less. This is the reason why amount of Insolation decreases from equator towards poles.
Question: How does carbon dioxide create green house effect?
Answer: Crbon dioxide creates greenhouse effect by trapping the heat radiated from the earth.
Question: What is the significance of greenhouse gas?
Answer: Without the greenhouse gas the earth would have been too cold to line in.
Question: What happens when air is heated?
Answer: When air is heated, it expands, becomes lighter and goes up.
Question: What is the nature of cold air?
Ans. It has tendency to go down.
Question: Why do green plants use carbon dioxide?
Answer: Green plants use carbon dioxide to make their food and release oxygen.
Question: What is an important feature of Stratosphere?
Answer: Stratosphere contains a layer of ozone gas.
Question: How is ozone important for us?
Answer: It protects us from the harmful effect of the sun rays.
Question: What is temperature?
Answer: The degree of hotness and coldness of the air is known as temperature.
Question: What is Insolation?
Answer: Insolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth.
Question: Why is there no air pressure on the moon?
Answer: There is no air on the moon and therefore no air pressure.
Question: Where is air pressure highest?
Answer: Air pressure is highest at the sea level.
Question: How does air move?
Answer: Air moves from high pressure areas to low pressure areas.
Question: Name three types of winds.
Answer:
- Permanent winds
- Seasonal winds
- Local winds.
Question: What is the hot and dry wind of northern planes of India called?
Answer: It is called loo.
Question: What is called humidity?
Answer: Moisture in the air at any time is called humidity.
Question: Why do we feel uncomfortable on a humid day?
Answer: It is because sweat from our body does not evaporate easily.
Question: How is flooding of low lying areas caused?
Answer: When trees on hill sides are cut, rainwater flows down the bare mountains. This causes flooding of low lying areas.
Question: Name various forms of precipitation.
Answer:
- Rain
- Snow
- Sleet
- Hail
Question: How is a wind named?
Answer: A wind is named after the direction from which it blows.
Question: Give an account of the composition of the atmosphere.
Answer: Our atmosphere is composed of mainly two gases—nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%). Other gases like carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, orgon and hydrogen are found in lesser quantities. Apart from these gases, tiny dust particles are also present in the air.
Question: How do Bacteria help plants use nitrogen?
Answer: Nitrogen is essential for the survival of plant. But plants cannot take nitrogen directly from the air. Bacteria, that live in the soil and roots of some plants, take nitrogen from the air and change its form so that plants can use it.
Question: How does nature balance our life? What is the result if this balance is disturbed?
Answer: Green plants use carbon dioxide to make their food and release oxygen. Humans or animals release carbon dioxide. The amount of carbon dioxide released by humans or animals seems to be equal to the amount used by the plants which make a perfect balance. But this balance is disturbed by burning of fuels, which add billions of tons of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. As a result, the increased volume of carbon dioxide is affecting the earth’s weather and climate.
Question: Why is temperature in cities much higher than that of villages ?
Answer: In cities we find high rise buildings. The concrete and metals in these buildings and the asaphalt of roads get heated up during the day. This heat is released during the night.
Another reason is that the crowded high rise buildings of the cities trap the warm air and thus raise the temperature of the cities.
Question: Write a short note on the distribution of air pressure in atmosphere.
Answer: Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface. As we go up the layers of atmosphere, the pressure falls rapidly .The air pressure is highest at the sea level and decreases with height. Horizontally the distribution of air pressure is influenced by temperature of air at a given place. In areas where temperature is high the air gets heated and rises. This creates a low pressure area. In areas having lower temperature, the air is cold, hence, it is heavy. Heavy air sinks and creates a high pressure area.
Question: Why do astronauts wear special protective suits when they go to the moon?
Answer: Astronauts wear special protective space suits filled with air when they go to the moon. If they did not wear these space suits, the counter pressure exerted by the body of the astronauts would make the blood vessels burst. The astronauts would bleed.
Question: How is rainfall important for us ? What happens when there is excess rain?
Answer: Rainfall is very important for the survival of plants and animals. It brings fresh water to the earth’s surface. If rainfall is less, there is water scarcity which sometime causes drought like situation. If there is excess rain, floods take place which make the life of the affected people miserable.
Question: Give an account of the different layers of the atmosphere.
Answer: Our atmosphere has five different layers. They are:
- Troposphere: This is the most important layer of the atmosphere with average height of 13 km from the earth. It is in this layer that we find the air that we breathe. Almost all the weather phenomena such as rainfall, fog and hailstorm occur here.
- Stratosphere: This layer extends up to a height of 50 km. It presents the most ideal conditions for flying airplanes. It contains a layer of ozone gas which protects us from the harmful effect of the sun rays.
- Mesosphere: This layer extends up to the height of 80 km. Meteorites bum up in this layer on entering from the space.
- Thermosphere: In this layer temperature rises very rapidly with increasing height. Ionosphere is a part of this layer. It extends between 80 – 400 km. This layer helps in radio transmission. Radio waves transmitted from the earth are reflected back to the earth by this layer.
- Exosphere: It is the uppermost layer where there is very thin air. Light gases such as helium and hydrogen float into the space from here.
Question: What is wind? Mention its different types.
Answer: Wind is the movement of air from high pressure area to low pressure areas. It is divided into three types:
- Permanent winds: The trade winds, westerlies and easterlies are the permanent winds. These blow constantly throughout the year in a particular direction.
- Seasonal winds: These winds change their direction in different seasons. For example: monsoons in India.
- Local winds: These winds blow only during a particular period of the day or year in a small area. For example: land and sea breeze. Loo is a local wind which hot and dry and blow in the northern plains of India during summers.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students