Question: How are fuels classified on the basis of their physical state? Give two examples of each.
Answer: Fuels can be classified on the basis of their physical state as solid, liquid and gas. On this basis, fuels can be of the following types:
- Solid fuels: Some solid fuels are wood, coal, cattle-dung cakes, etc.
- Liquid fuels: Some of the liquid fuels are kerosene, LPG , petrol, diesel, etc.
- Gaseous fuels: Some of the gaseous fuels are CNG, coal gas, water gas, producer gas, biogas, etc.
Question: How is burning of fossil fuels thought to be related to global warming?
Answer: Combustion of fossil fuels adds carbon dioxide and carbon mono oxide in to air. This trap the sunlight and increase the average temperature of atmosphere called the greenhouse effect and cause global warming. Global warming melts ice caps
that causes flood.
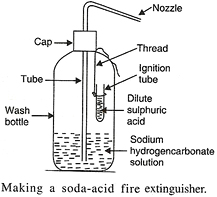
Question: Explain, with the help of a labelled diagram, how a soda-acid type fire extinguisher works.
Answer: The simplest fire extinguisher is the soda-acid type fire extinguisher. In this, the property of acids to liberate carbon dioxide on reacting with carbonates and bicarbonates of metals is utilized. As the gas carbon dioxide is evolved with brisk effervescence, it extinguishes the fire when released over it.
There are three parts in a fire extinguisher: Container, Bottle and Knob
The container of a fire extinguisher is cylindrical in shape. It contains sodium bicarbonate solution. The small bottle contains concentrated Sulphuric acid. This bottle is attached to the knob.
For the chemical reaction to take place, the knob is struck. The bottle breaks and sulphuric acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate liberating large amount of CO2 gas with great force. It forms a blanket around the fire, cutting off the air supply, due to which the fire gets extinguished.
2NaHCO3 + H2SO4 ——-> Na2SO4 + 2H2O + 2CO2
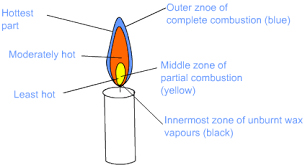
Question: Name the different zones of a candle flame. Give details of the conditions in each zone.
Answer: Candle flame: Light a candle and observe its flame. The flame has three main zones depending on the amount of air it receives. The zones have different colours.
- Non-luminous zone or the zone of complete combustion is the hottest part of the candle flame. Because of adequate supply of oxygen, complete combustion occurs. Therefore, no residue is left on an object placed in this zone. The flame appears blue. It is the outermost zone of the flame.
- Luminous zone or the zone of incomplete combustion is moderately hot. The wax vapours do not burn completely as the supply of oxygen is inadequate. It leaves a black soot and other residues on an object placed here. The carbon particles glow emitting a yellow light. It is the middle zone of the flame.
- Dark zone or the zone of no combustion is the least hot. It covers the area surrounding the wick containing unburnt vapours produced by the melting of wax. Here the wax vapours do not come in contact with oxygen, hence do not burn. It is the innermost zone of the flame.
Question: What are the characteristics of a good fuel?
Answer: The heat liberated by a fuel is measured in Kilojoules. A fuel is considered good if it:
- has a low ignition temperature.
- produces a large quantity of heat, that its calorific value is high,
- has a moderate rate of combustion,
- is safe to store, handle and transport,
- does not cause pollution,
- leaving behind little or no residue after being burnt,
- is cheap and easily available
Natural gas best meets all these conditions.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students



Hi! I’m Gauri Bharti of class 8th I have problems in some questions but now I clearly answered the questions. Tnq u!