Question: What is the ‘blind spot’ of the eye?
Answer: Blind spot is the region of the retina at the junction of the optic nerve and the retina. There are no sensory cells at this spot, hence any image formed here cannot be seen.
Question: What is the difference between the displacement produced by a rectangular glass slab in a ray of light and the deviation produced by a glass prism?
Answer:
Question: Explain the term ‘spectrum’. Why does a glass prism split white light into its constituent colours?
Answer: The splitting up of white light into its constituent colors is called dispersion. The patch of colored light obtained due to dispersion through a glass prism on the screen is known as a spectrum. A glass prism splits white light into its constituent colors because of deviation. Different colors of light are deviated by different amounts. Hence the colors separate out on emerging from the prism.
Question: Distinguish between converging and diverging lenses.
Answer:
Question: Define the following terms for a lens: a. optical centre b. principal axis c. principal focus d. focal length
Answer:
- Optical centre: The optical centre of a lens is a point on the principal axis such that a ray passing through it does not undergo any deviation.
- Principal axis: A straight line passing through the centres of curvature C1 and C2 of the two surfaces of the lens is called the principal axis.
- Principal focus: If a beam of light parallel to the principal axis is incident on a converging lens, the rays of light after passing through the lens converge at a point F. This point is called the principal focus or simply the focus of the lens.
- Focal length: The distance between the optical centre and the focus of a lens is called the focal length of the lens.
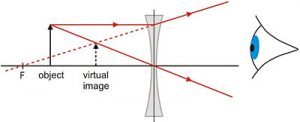
Question: Why does a concave lens always form a virtual image of an object? Draw a diagram to illustrate this.
Answer: Image formed by a concave lens: The rays falling on a concave lens, after refraction, always diverge. Therefore, no matter where the object is kept, a diverging lens always forms a virtual image, which is erect and smaller in size than the object. It is formed between the optical centre and the focus, on the same side of the lens as the object.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students



I want full pdf page