Question: A body does 1200 J of work in 2 min. Calculate its power.
Answer:
P = Work/Time
1200/120
= 10 watts
Question: How many Joules are these in one kilo-watt hour?
Answer:
= 3.6 × 106J
Question: A trolley pushed along a road with a force of 400 N through a distance of 60 m in 1 min. Calculate power.
Answer:
Work = F × S
= 400 × 60
= 24000 J
Power = W/T
= 24000/60
400 watts.
Question: A man weighting 500 N Care-id a load of 100 N up a flight of stairs 4 m high in 5 s what is the power.
Answer: Total Force = 500 + 100 N
= 600 N
Distance = 4 m.
work = F × S
= 600 × 4
= 2400 J
Power = W/T
= 2400/5
= 480 watts.
Question: The power output of an engine is 3 kw. How much work it does in 20 s?
Answer: Power = W/T
3000 = W/20
60000 = W
= 60 KJ
Question: An electric heater used 600 KJ of electrical energy in 5 min. Calculate power rating.
Answer:
P = W/T
P = 600000/5 × 60
= 2000 W
= 2 KW
Question: Calculate energy in joules does a 100 watt lamp consume.
Answer:
(1). in 1 second
P = W/T
100 = W/1
Work = 100 J
(2). in 1 minute
P = W/T
100 = W/60
W = 6000 J
Question: Five electric tans of 120 watts are used for 4 hrs Calculate energy consumed in Kw-h.
Answer:
Power = 120 watts
120/1000 kilowatts
Total Power = 0.12 Kw × 5 = 0.6 Kw
Power = Energy/Time
0.6 = Energy/4 her
Energy = 0.6 × 4
= 2.4 Kwh
Question: A bulb lights up when connected to a paltry. State energy change.
Answer:
- In battery: Chemical energy to electrical energy.
- In bulb: Electrical energy to light energy.
Question: A car of weight 20000 N clumps up a hill at a steady speed of m/s gaining a height of 120 m in 100 s.
Answer:
(1). Work done:
W = F × S
= 20000 × 120
= 2400000
= 2400 KJ
(2). Power:
P = W/T = 2400/100
= 24 Watts
Question: (I).What do you understand by the term “transformation of energy” Explain with example.
(II). Explain transformation of energy in
(1). a ball thrown upwards. (2). A stone dropped from the roof.
Answer: (I). Suppose a stone is lying on the roof of a house. In this position it has potential energy when the stone is dropped from the roof, it starts moving downwards towards the ground and the potential energy goes on decreasing (because weight is decreasing) but its kinetic energy goes on increasing (because its velocity goes on increasing). And finally, all the potential energy gets transformed into kinetic energy. When it reaches ground. The change of one form of energy into another form of energy is known as transformation of energy.
(II).
- Kinetic energy to potential energy.
- Potential energy to kinetic energy.
Question: (1). What is the meaning of ‘kWh’? What Quantity does it represent?
(2). How much energy in kWh is consumed by an electrical appliance of 1000 watts when it is switched on for 60 mins.
Answer: (1). One kilo watt-hour is the amount of energy consumed of when an electrical appliance of 1000 watts is used for 1 hour. It is the commercial unit of energy.
(2).
1000 watts = 1000/1000 Kilowatts
= 1 Kilowatts
Power = Energy/Time
1 = Energy/1 hr
Energy = 1 × 1
= 1 kwh
Question: A family consumes 650 units in a mouth. How much electricity is it in Joules.
Answer:
1 kwh = 3600000 J
650 kwh = 650 × 3600000 J
= 2.34 × 109 J.
Question: A boy weighting 40 kg carries a box weighting 20 kg, 15 m high in 25 seconds. Calculate power (g = 10 m/s2 )
Answer:
Work = M × g × h
= (40 + 20) × 10 × 15
= 60 × 10 × 15
= 9000
= 9 k Joules
Power = W/T
= 900/25
= 360 watts
Question: (I). State and explain the law of conservation of energy with example.
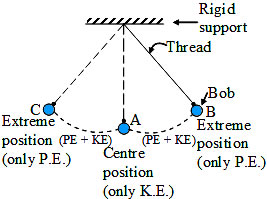
(II). Explain how, the total energy of swinging pendulum at any instant of time remains conserved. Draw a labelled diagram.
Answer: (I). Law of conservation of energy states that, Energy in the isolated system remains constant.
Now, for the conversions you have provided, light energy is nothing but collection of electromagnetic waves. These waves carry energy proportional to their frequency. Light gets reflected, transmitted or absorbed. In case of absorption there is conversion of energy. The constituting atoms or molecules vibrate, translate or rotate with greater energy which they get from incident light. This increased energy in object can be stored or given out in some form.
Heat transfer occurs by convection, conduction or radiation. For radiation, same as light. Similarly, transfer of heat energy by convection or conduction is microscopic and depends on object receiving, whether to store or give out this energy in different form.
(II). A Swinging Pendulum:
- When the pendulum bob is at position B it has only potential energy but no kinetic energy.
- As the bob starts moving goes on decreasing but kinetic energy increases.
- When the bob reaches A, it has only kinetic energy, no potential energy.
- As the bob goes from A to C, KE energy decreases but potential energy increases.
- On reaching the extreme position, C the bob stops for a very small instant of time, So at C the bob has only potential energy (but no kinetic energy).
At all other intermediate positions the energy of pendulum bob is partly instant partly kinetic. But the total energy of the swinging pendulum at any instant of time remains the same (or conserved).
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students