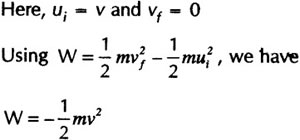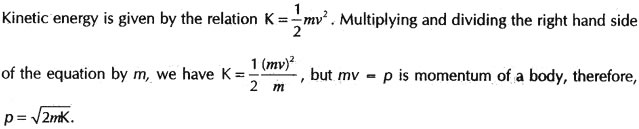Question: A battery lights a bulb. Describe the energy changes involved in the process.
Answer: Within the electric cell of the battery the chemical energy changes into electrical energy. The electric energy on flowing through the filament of the bulb, first changes into heat energy and then into the light energy.
Question: What is the work done by the force of gravity on a satellite moving round the earth? Justify your Answer:
Answer: The work done by the force of gravity on the satellite is zero because the force of gravity acts at right angles to the direction of motion of the satellite. Therefore, no displacement is caused in the direction of applied force. The force of gravity only changes the direction of motion of the i satellite.
Question: Can there be displacement of an object in the absence of any force acting on it? Think;discuss this question with your friends and teacher.
Answer: The answer is both Yes and No. Yes, because when an object moves in deep space from one point to another point in a straight line, the displacement takes place, without the application of force. No, because force cannot be zero for displacement on the surface of earth. Some force is essential.
Question: A person holds a bundle of hay over his head for 30 minutes and gets tired. Has he done some work or not? justify your Answer:
Answer: The person does not do work because no displacement takes place in the direction of applied force as the force acts in the vertically upward direction.
Question: An object of mass, m is moving with a constant velocity, v. How much work should be done on the object in order to bring the object to rest?
Answer: Work done to bring the object to rest is equal change in kinetic energy of the object.
Question: Soni says that the acceleration in an object could be zero even when several forces are acting on it. Do you agree with her? Why?
Answer: Yes, we do agree when the number of forces act on a body, such that they constitute balanced forces, then net force acting on the body is zero. In such a situation no acceleration acts on the object.
Question: A freely falling object eventually stops on reaching the ground. What happens to its kinetic energy?
Answer: The KE on reaching the ground changes into heat energy, sound energy etc. and, therefore, gets dissipated in air.
Question: What kinds of energy transformations take place at a thermal power station?
Answer: At a thermal power station, the chemical energy of coal is changed into heat energy which is further changed into electrical energy with the help of an electric generator.
Question: Name the transformation of energy involved in the following cases:
- When a body is thrown upwards.
- When a body falls from the top of a hill.
- When coal burns.
- When a gas bums.
- When water falls from a height.
Answer:
- Kinetic energy into potential energy.
- Potential energy into kinetic energy.
- Chemical energy into heat energy.
- Chemical energy into heat energy.
- Potential energy into kinetic energy.
Question: What are the factors on which the work done depends?
Answer: The work done by a force depends upon:
- The magnitude of the force.
- The magnitude of the displacement and
- The angle between force and displacement.
Question: How are kinetic energy and momentum related ?
Answer:
Question: What is the work done by a coolie walking on a horizontal platform with a load on his head ?
Answer: In order to balance the load on his head, the coolie applies a force on it in the upward direction, equal to its weight. His displacement is along the horizontal direction. Thus, the angle between force F and displacement is 90°. Therefore, work done W = FS cos θ = FS cos 90° = 0.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students