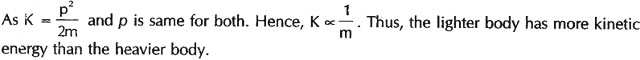Question: A light and a heavy body have the same momentum. Which one will have greater kinetic energy?
Answer:
Question:
- Can a body have energy without having momentum? Explain.
- Can a body have momentum without having energy? Explain.
Answer:
Question: When an arrow is shot from its bow, it has kinetic energy. From where does it get the kinetic energy?
Answer: A stretched bow possesses potential energy on account of a change in its shape. To shoot an arrow; the bow is released. The potential energy of the bow is converted into the kinetic energy of the arrow.
Question: A spring which has been kept compressed by tying its ends together is allowed to be dissolved in an acid. What happens to the potential energy of the spring?
Answer: The PE of the spring gets converted into KE of acid molecules whose temperature rises.
Question: justify giving proper reasoning whether the work done in the following cases is positive or negative:
- Work done by a man in lifting a bucket out of a well by means of a rope tied to the bucket.
- Work done by gravitational force in the above case.
- Work done by friction on a body sliding down an inclined plane.
- Work done by an applied force on a body moving on a rough horizontal plane with uniform velocity.
- Work done by resistive force of air on a vibrating pendulum in bringing it to rest.
Answer:
- Work done is positive as the bucket moves in the direction of force applied by the man.
- Work done by the gravitational force is negative, as the bucket moves upwards i.e., opposite to the gravitational force.
- Work done is negative, as frictional force acts opposite to the direction of motion of the body.
- Work done is positive because applied force acts along the same direction as the direction of motion of the body.
- Work done is negative because the resistive force of air always acts opposite of the direction of motion of the vibrating pendulum.
Question: What is the work done by a coolie walking on a horizontal platform with a load on his head?
Answer: In order to balance the load on his head, the coolie applies a force on it in the upward direction, equal to its weight. His displacement is along the horizontal direction. Thus, the angle between force F and displacement is 90°. Therefore, work done W = FS cos θ = FS cos 90° = 0.
Question: The work done in lifting a box on to a platform does not depend upon how fast it is lifted up.Explain your answer giving proper reasoning.
Answer: The work done (W) in lifting a box through a distance (S) against the gravitational force (F) is given by W = FS. Hence, it is obvious that it is independent of the rate at which the box is lifted.
Question: Is it possible that a body be in accelerated motion under a force acting on the body, yet no work is being done by the force ? Explain your answer giving a suitable example.
Answer: Yes, it is possible, when the force is perpendicular to the direction of motion. The moon revolving round the earth under the centripetal force of attraction of the earth, but earth does no work on the motion.
Question: A body moves along a circular path. How much work is done in doing so? Explain.
Answer: In case of a body moving along a circular path, the force (centripetal) is always along the radius while displacement is tangential. Hence, work done W = FS cos 90° = 0 as angle between F and S is 90°.
Question: A man rowing a boat upstream is at rest with respect to the shore. Is he doing work?
Answer: The man is doing work relative to the stream because he is applying force to produce relative motion between the boat and the stream. But he does zero work relative to the shore as the displacement relative to the shore is zero.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students