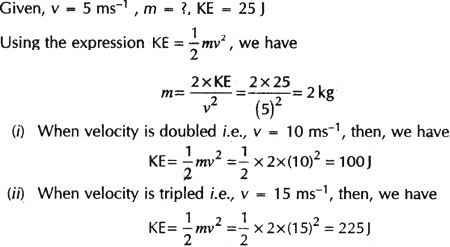Question: What type of energy is stored in the spring of a watch?
Answer: When we wind a watch, the configuration of its spring is changed. The energy stored in the spring is obviously potential in nature (elastic potential energy to be more accurate).
Question: What happens to the kinetic energy when:
- the mass of the body is doubled at constant velocity?
- the velocity of the body is doubled at constant mass?
- the mass of the body is doubled but the velocity is reduced to half?
Answer:
Question: When a constant force is applied to a body moving with constant acceleration, is the power of the force constant? If not, how would force have to vary with speed for the power to be constant?
Answer: We know that (P) = force (F) × velocity (V). Since the body is moving with acceleration, V changes and as a result of that of that P also changes, F being constant. For P to be constant, FV = constant or F ∞ 1/V.
Thus, as V increases, F should decrease to keep P constant.
Question: A spring which is kept compressed by tying its ends together is allowed to be dissolved in an acid. What happens to the potential energy of the spring?
Answer: The potential energy of the spring gets converted into heat energy (kinetic energy of acid molecules). Due to this heat, the temperature of the acid rises.
Question:
- Define power. Give its SI unit.
- Taking the example of a simple pendulum, explain the variations in the forms of energy and the; inter-conversions involved.
Answer:
- Power is defined as the rate of doing work. Its SI unit is watt.
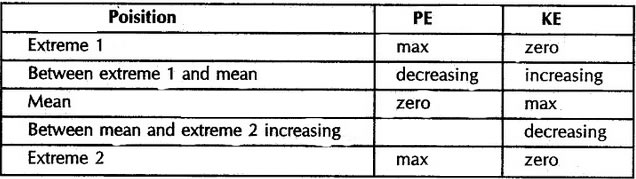
- For a simple pendulum, the inter-conversion of energy is as shown in the table below :
Question:
- How much work is done when a force of 1 N moves a body through a distance of 1 m in its direction?
- Is it possible that a force is acting on a body but still the work done is zero? Explain giving one example.
Answer:
- 1 J of work is done.
- Yes, it is possible when force acts at right angles to the direction of motion of the body. Example Gravitational force of earth acts on a satellite at right angles to its direction of motion.
Question:
- What is meant by potential energy? Is potential energy vector or scalar quantity?
- Give one example of a body having potential energy.
Answer:
- The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its position or configuration. It is a scalar quantity.
- Stretched string of a bow.
Question: When is the work done by a force said to be negative? Give one situation in which one of the forces acting on the object is doing positive work and the other is doing negative work.
Answer: We know that work done W = FS cos 0, where 0 is the angle between F and S. Clearly, W will be -ve, if 0 is between 90° and 180° because then cos 0 will be -ve. Consider the case of a body falling under gravity. The body experiences an upward frictional force and downward force due to gravity. Since the body is moving downwards, the work done by force to gravity will be +ve but that is against the upward thrust will be -ve.
Question:
- Is it possible that a body be in accelerated motion under the action of a force, yet no work is being done by the force? Explain with an example.
- Two bodies of masses m, and m2 have equal kinetic energies. What is the ratio of their linear momenta?
Answer:
(a) Yes, it is possible in the case of a body moving in a circular path with a speed v. The body has a centripetal acceleration directed along the radius of the circular path. The displacement is, however, tangential to the radius i.e., 0 = 90°. Thus, work done, W = FS cos 90° = 0.
Question: The kinetic energy of an object of mass ‘m’ moving with a velocity of 5 ms-1 is 25 J. What will be its kinetic energy when its velocity is doubled? What will be its kinetic energy when its velocity is increased three times?
Answer:
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students