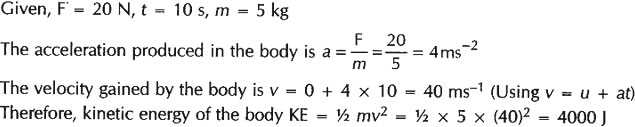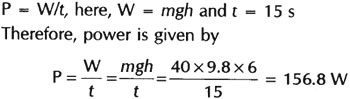Question: A block of mass 5 kg is lying bn a frictionless table. A force of 20 N is applied on it for 10 seconds. Calculate its kinetic energy.
Answer:
Question: A girl of mass 40 kg climbs a rope 6 m long at constant speed in 15 seconds. What power she expands during the climb?
Answer:
Question: A man weighing 70 kg caries a weight of 10 kg to the top 6f a tower 100 m high. Calculate the work done.
Answer:We know that work done is given by W = FS = mgh i.e., change in potential energy, therefore, we have W = mgh = (70 + 10) x 9.8 x100 = 78400 J
Question: Calculate the kinetic energy of a body of mass 2 kg moving with a velocity of 0.1 ms-1.
Answer:
Question: Find the velocity of a body of mass 100 g having a kinetic energy of 20 J.
Answer:
Question: A man drops a 10 kg rock from the top of a 5 m ladder. What is its kinetic energy when reaches the ground? What is its speed just before it hits the ground?
Answer:
Question: Which would have greater effect on kinetic energy of an object – doubling the mass, or doubling the velocity?
Answer: We know that KE∝ m, KE ∝ v2
Therefore, by doubling the mass, the kinetic energy doubles, while by doubling the velocity, the kinetic energy increases four times. Therefore, doubling the velocity will have a greater effect on the kinetic energy of an object.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students