Question:
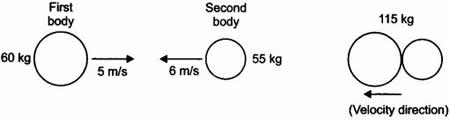
Two bodies as shown in the figure collide with each other and join thereafter. With what velocity will they move after combining together?
Answer:
Question: Explain Newton’s second law of motion and with the-help of an example show how it is used in sports.
Answer: Newton’s second law of motion: The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of the force.
Let us assume: Object of mass m, is moving along a straight line with an initial velocity ‘u’, It is uniformly accelerated to velocity v in time ‘t by the application of force,

In cricket field, the fielder gradually pulls his hands backward while catching a ball. The fielder catches the ball and gives swing to his hand to increase the time during which the high velocity of the moving ball decreases to zero.
The acceleration of the ball is decreased and therefore the impact of catching the fast moving ball4s reduced.
If not done so, then the fast moving ball will exert large force and may hurt the fielder.
Question: State all 3 Newton’s law of motion. Explain inertia and momentum.
Answer:
Newton’s I law of motion: An object remains in a state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force.
Newton’s II law of motion: The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of the-force.
Newton’s III law of motion: To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction and they act on two different bodies.
Inertia: The natural tendency of an object to resist a change in their state of rest or of uniform motion is called inertia.
Momentum: The momentum of an object is the product of its mass and velocity and has the same direction as that of the velocity. Its S.I. unit is kgm/s. p = m x v
Question: Define force. Give its unit and define it. What are different types forces?
Answer: Force: It is a push or pull on an object that produces acceleration in the body on which it acts.
A force can do 3 things on a body
(a) It can change the speed of a body.
(b) It can change the direction of motion of a body.
(c) It can change the shape of the body.
The S.I. unit of force is Newton.
Newton: A force of one Newton produces an acceleration of 1 m/s2 on an object of mass 1 kg.
1N = 1kg m/s2
Types of forces:
- Balanced force: When the forces acting on a body from the opposite direction do not change the state of rest or of motion of an object, such forces are called balanced forces.
- Unbalanced force: When two opposite forces acting on a body move a body in the direction of the greater force or change the state of rest, such forces are called as unbalanced force.
- Frictional force: The force that always opposes the motion of object is called force of friction.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students




