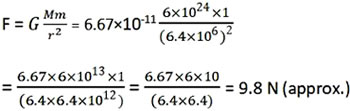Question: How does the force of gravitation between two objects change when the distance between them is reduced to half?
Answer: According to Universal Law of gravitation, the gravitational force of attraction between any two objects of mass M and m is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of distance r between them
So, force F is given by
Hence, if the distance is reduced to half, then the gravitational force becomes four times larger than the previous value.
Question: Gravitational force acts on all objects in proportion to their masses. Why then, a heavy object does not fall faster than a light object?
Answer:
All objects fall on ground with constant acceleration, called acceleration due to gravity (in the absence of air resistances). It is constant and does not depend upon the mass of an object. Hence, heavy objects do not fall faster than light objects.
Question: What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a 1 kg object on its surface? (Mass of the earth is 6 × 1024 kg and radius of the earth is 6.4 × 106 m).
Answer:
Given that,
Mass of the body, m= 1 kg
Mass of the Earth, M= 6×1024 kg
Radius of the earth, R= 6.4×106 m
Now, magnitude of the gravitational force (F) between the earth and the body can be calculated.
Question: The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why?
Answer: According to the universal law of gravitation, two objects attract each other with equal force, but in opposite directions. The Earth attracts the moon with an equal force with which the moon attracts the earth.
Question: If the moon attracts the earth, why does the earth not move towards the moon?
Answer: The Earth and the moon experience equal gravitational forces from each other. However, the mass of the Earth is much larger than the mass of the moon. Hence, it accelerates at a rate lesser than the acceleration rate of the moon towards the Earth. For this reason, the Earth does not move towards the moon.
Question: What happens to the force between two objects, if
(i) the mass of one object is doubled?
(ii) the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
(iii) the masses of both objects are doubled?
Answer: From Universal law of gravitation, force exerted on an object of mass m by earth is given by
So as the mass of any one of the object is doubled the force is also doubled.
(ii) The force F is inversely proportional to the distance between the objects. So if the distance between two objects is doubled then the gravitational force of attraction between them is reduced to one fourth (1/4) of its original value.
Similarly, if the distance between two objects is tripled, then the gravitational force of attraction becomes one ninth (1/9) of its original value.
(iii) Force F is directly proportional to the product of both the masses. So, if both the masses are doubled then the gravitational force of attraction becomes four times the original value.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students