Question: Write three steps taken by the government for the protection and conservation of great biological diversity of India.
Answer:
- Various biosphere reserves have been set up in various parts of India. For example the Nilgiri at Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Kerala, Nanda Devi in Uttarakhand, etc.
- About 99 national parks, 513 wildlife sanctuaries, and 35 zoological gardens have been set up. Financial and technical assistance is provided to many Botanical Gardens set up by the government.
Question: Describe the altitude zones of vegetation in the mountainous regions.
Or
“The mountainous region of India exhibits a succession of natural vegetation belts from tropical to tundra types, all compressed into an altitude of six kilometers or so”. Elaborate the above statement with four examples from different latitudinal belts.
Or
Describe the major vegetation zones of the Himalayan region.
Or
In mountainous area, there is change in natural vegetation due to decrease in temperature. Justify giving examples from different zones.
Answer: In the Himalayan region of our country, the vegetation differs according to the height.
- In the foothill, (the Shiwalik) are tropical deciduous forests. ‘Sal’ is the most important species of economic significance.
- The zone with altitude 1000 m – 2000 m consists of evergreen forests. Beech, chestnut, oak, ash, etc., are the main trees. These at a higher altitude are replaced by ‘chir’ and ‘chil’.
- The zone between 1500m – 3000 m includes pine, cedar, silver fir and spruce. They are the famous coniferous trees, typical of the dry temperate region found in the inner Himalayan region.
- At the height of 3600 m or more, shrubs, scrubs, and grasses of alpine variety are found.
Question: Write three steps taken by the government for the protection and conservation of great biological diversity of India.
Or
Give any three steps taken by the government of India to protect the flora and fauna.
Answer:
- Various biosphere reserves have been set up in various parts of India. For example, the Nilgiri at Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala, Nanda Devi in Uttarakhand etc.
- About 100 national parks, 515 wildlife sanctuaries, and 35 zoological gardens have been set up.
- The endangered species are being identified and special efforts are being made to preserve them. For example: Tiger Project’.
- Killing of wildlife has been banned and special forest officers have been appointed.
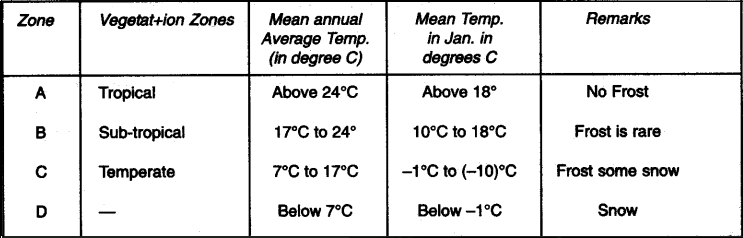
Question: Carefully study the given table and answer the following questions:
Temperature Characteristics of the vegetation Zones table:
(i) Is there any relationship between temperature and type of vegetation?
Answer: Yes, the fall in temperature affects the type of vegetation and its growth and changes it from tropical to subtropical.
(ii) Identify the type of vegetation you can expect in zone D.
Answer: Alpine.
(iii) Is temperature the only criteria for all types of vegetation?
Answer: No, vegetation also depends on rainfall, humidity and altitude.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students