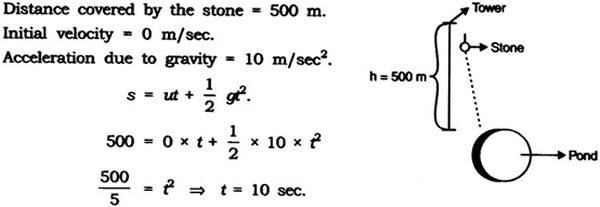Question: Give two practical applications of reflection of sound waves.
Answer: Reflection of sound is used in megaphones, horns and musical instruments such as trumpets and shehna. It is used in stethoscope for hearing patient’s heartbeat. Ceilings of the concert halls are curved, so that sound after reflection reaches all comers of the hall. (Any two practical applications can be written).
Question: A stone dropped from the top of a tower 500 m high into a pond of water at the base of the tower. When is the splash heard at the top? Giving, g = 10 ms-2 and speed of sound = 340 m s-1.
Answer:
Question: A sound wave travels at a speed of 339 ms-1. If its wavelength is 1.5 cm, what is the frequency of the wave? Will it be audible?
Answer:
Question: What is reverberation? How can it be reduced?
Answer: The persistence of sound in an auditorium is the result of repeated reflections of sound and is called reverberation.
To reduce the undesirable effects due to reverberation, roofs and walls of the auditorium are generally covered with sound absorbent materials like compressed fiberboard, rough plaster or draperies. The seat materials are also selected having sound absorption properties.
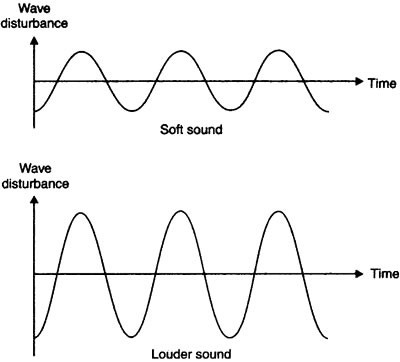
Question: What is loudness of sound? What factors does it depend on?
Answer: The loudness of sound is determined by its amplitude. The amplitude of the sound wave depends upon the force with which an object is made to vibrate. Loud sound can travel a larger distance as it is associated with higher energy. A sound waves spreads out from its source. As it moves away from the source its amplitude as well as its loudness decreases.
Question: Explain how bats use ultrasound to catch a prey.
Answer: Bats search out its prey by emitting and detecting reflections of ultrasonic waves. The high-pitched ultrasonic squeaks of bat are reflected from the obstacles or prey and return to bat’s ear. The nature of reflection tells the bat where the obstacle or prey is and what it is like.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students