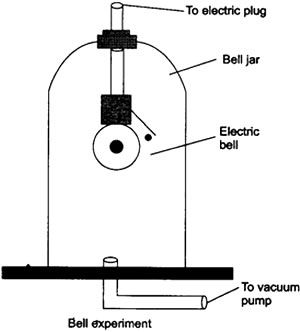
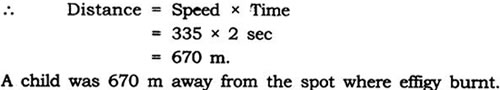Question: Sound cannot travel in vacuum. Describe an experiment to demonstrate this.
Answer: Sound is a mechanical wave and needs a material medium to propagate. It cannot travel in vacuum and can be shown by the following experiment.
- Take an electric bell and an airtight glass bell jar. The electric bell is suspended inside the airtight bell jar. Switch ‘ON’ the electric bell.
- Now, connect the bell jar to vacuum pump.
- Pump out the air from the jar, the sound becomes fainter, although the same current passes through the bell.
- Pump out some more air from the jar, a very feeble sound is heard.
- When the air is completely removed from the jar, no sound is heard.
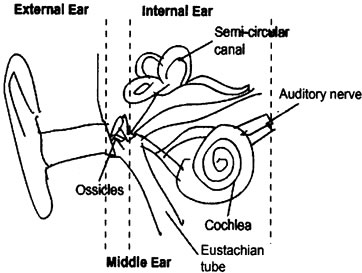
Question: Explain the structure of the human ear with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
(I) Outer Ear: Pinna, auditory canal and tympanic membrane.
- Pinna: It collects the sound from the surroundings.
- Auditory Canal: The sound waves collected passes through this canal.
- Tympanic Membrane: It is a thin membrane which receives the vibrations of sound. A compression reaches the eardrum, the pressure on the outside of the membrane increases and pushes the eardrum inward, and moves out when the rarefaction reaches.
(II) Middle Ear: Consists of three small bones called hammer, anvil and stirrup. The vibrations are received by these three bones and the strength of vibrations is increased i.e., the sound is amplified and passed to inner ear.
(III) Inner Ear: It consist of cochlea and auditory nerve.
Chochlea receives the amplified vibrations and convert them into electrical signals. These electrical signals are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve and the brain interprets the signals as sound.
Question: Given that sound travels in air at 340 m/sec, find the wavelength of the waves in air produced by 20 kHz sound source. If the same source is put in a water tank, what would be the wavelength of the sound waves in water? (Speed of sound in water = 1480 m/s.)
Answer:
Question: A child watching Dussehra celebration from a distance sees the effigy of Ravana burst into flames and hears the explosion associated with it 2 sec after that. How far was he from the effigy if the speed of sound in air that night was 335 m/sec?
Answer:
Question: What is reverberation? What will happen if the reverberation time in a big hall is two long? How can reverberation in a big hall or auditorium be reduced?
Answer: The persistence of sound in a big hall due to repeated reflection from the walls, ceiling and floor of the hall is called re-vibration. If the re-vibration is too long, then the sound becomes blurred, distorted & confusing due to overlapping of different sounds. These excessive re-vibrations in in big halls can be reduced by using various types of sound absorbing materials.
Question: What is a megaphone, bulb horn and a stethoscope? Name the principle on winch they work?
Answer: A megaphone is a large cone shaped (or funnel shaped) device for amplifying and directing the voice of a person who speaks into it.
A bulb horn is a cone-shaped wind instrument which is used for signalling in bicycles, cars, buses, trucks & boats etc. Stethoscope is a medial instrument used by the doctors for listening to the sounds produced within the human body, mainly in the heat and the lungs.
The principle in all the three instruments is ‘multiple reflection of sound’.
Question: What is meant by ‘loudness’, ‘pitches of a sound’ and ‘quality of a sound’? On what factor does each of them depend?
Answer: The loudness of sound is a measure of the sound energy reaching the ear per second. It depends on the amplitude of sound waves.
The pitch is that characteristic of sound by which we can distinguish between different sounds of the same loudness. The pitch of a sound depends on the frequency of vibration.
Quality is that characteristic of musical sound which enables us to distinguish between the sounds of same pitch and loudness produced by different musical instruments and different singers.
Quality of musical sound depends on the shape of sound wave (wave form), frequencies and amplitude.
Question: How is it that bats are able to fly at night without colliding with other objects? Explain how, bats use ultrasound to catch the the prey?
Answer: Bats, emit high-frequency ultrasonic squeaks while flying and listen to the echoes produced by the reflection of their squeaks from the obstacles in their path. From the time taken by the echo to be heard bats can judge the distance of the objects in their path and hence avoid it by changing the direction-This is called echolocation.
Bats also catch their prey by the method of echolocation. It follows the same methods as explained above and judge the distance of the prey and catch it.
Question: What is meant by ‘reflection’ of sound’? What type of surfaces are the best for reflecting sound?
Answer:
- Bouncing back of sound when it strikes a hard surface is called reflection of sound. Hard surface are best for it.
- Name any two objects which are good reflectors of sound. Wall, Metal sheet and hard wood.
- State the laws of reflection of sound.
(i) The incidence sound wave, the reflected sound wave and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The angle of reflection of sound wave is always equal to the angle of incidence of sound.
Question: (1) What is an echo? How is echo formed?
(2) What is the minimum distance in air required from a sound reflecting surface in air required from a sound reflecting surface to hear an echo (at 20°C).
(3) A man standing 825 m away from a cliff (steep rock) their a gun. After how long will he hear its echo? Speed of sound in air is 33o m/s?
(1). The repetition of sound caused by the reflection of sound waves is called an echo.
(2). 17.2 m.
(3). Distance b/w man and cliff = 825
distance sound will travel = 825 × 2
= 1650 m.
speed of sound = 330 m/s
Time = D/s
1650/330 = 5 seconds.
Question: (1). What is ultrasound? What is the difference between ordinary sound and ultrasound?
(2). Write any three use of ultrasound.
Answer: (1). The sound having too frequency (above 20,000 Hz) are called ultrasonic sound or ultrasound where as they can hear ordinary sounds.
(2). Its applications are:
- They are used to break kidney stones into fine grains.
- They are used to monitor the development of forties inside the mother’s uterus.
- It is used detach flaws in metal blocks without damaging them.
Question: The audible range of frequencies of an average human ear is from 20 Hz to 20 kHz calculate the corresponding wavelengths (speed of sound in our is 344 ms-1).
Answer: Infrasonics:
f = 20 Hz
V = 344 ms-1
λ = ?
V = f × λ
344 = 20 × λ
344/20 = λ
Wavelength = 17.2 m.
λ = 1.36 m.
Ultrasonics:
f = 20,000 Hz
V = 344 ms-1
λ = ?
V = f × λ
344 = 20,000 × λ
344/20,000 = λ
Wavelength = 172/10000 = 0.0172 m.
So, audible wavelength range = 17.2 m. – 0.00172 m.
Question: (I)Define: (1). Echolocation (2). Echocardiography (3). Ultrasonography.
(II) Name an animal which navigates and finds food using echolocation.
(III) Which produces ultrasonic waves porpoise or whales.
Answer: (I).
- Echolocation: The method used by some animals to locate objects by hearing echos of their ultrasonic squeaks is called ‘echolocation’.
- Echocardiography: The use of ultrasound waves to investigate the action of the heart is called echocardiography.
- Ultrasonography: The techingve of offaining pictures of internal organs of the body by using echoes of ultrasound pulses is called ultrasonography.
(II). Bats
(III). Porpoises
Question: A sonar picks up a return signal after 3 seconds. How far is the object (speed of sound = 1440 m/s water).
Answer: Distance travelled = s × T = 3 × 1440
= 4320 m
Distance b/w object & sonar = 4320/2 = 2160 m.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students