Question: State the difference between bone and blood.
Answer: Bone:
- It is a hard tissue.
- It consists of osteocytes.
- It helps in movement and support of the body.
Blood:
- It is a liquid tissue.
- It consists of plasma, RBC, WBC and blood platelets.
- It helps in the transport of substances.
Question: Name all different types of tissues present in animal.
Answer: There are four main types of tissues present in animal.
- Epithelial tissue present on the outer and inner lining of the body.
- Muscular tissue are made up of muscles, help in movement.
- Connective tissue connects the different organs in the body.
- Nervous tissue consists of nerve cells and are present in the nervous system.
Question: Why is blood called connective tissue?
Answer: The blood is composed of cells and plasma. Plasma is a fluid and cells like red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are present in it. All these cells are connected due to plasma. It also transports food, water to different parts of the body and connects them.
Question: Name three types of muscle tissues and give function of each.
Answer: Three types of muscle tissues are:
- Striated muscle: These muscles show alternate light and dark bands or striations. They are involuntary and present in skeletal tissues,, help in movement of body and bones.
- Smooth muscle: These are involuntary muscles, control the movement of food in alimentary canal, contraction and relaxation of blood vessels. Present in iris, uterus etc.
- Cardiac muscle: These muscles are present in heart, help in the rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout the life.
Question: State the difference between simple tissues of plants.
Answer: The simple tissues of plants are:
Parenchyma:
- Their size, shape, and structure vary greatly.
- Encyclopedia Britannica, Inc.
- Parenchyma makes up the chloroplast-laden mesophyll (internal layers) of leaves and the cortex (outer layers) and pith (innermost layers) of stems and roots; it also forms the soft tissues of fruits.
Collenchyma:
- Collenchyma cells are elongated cells with irregularly thick cell walls that provide support and structure.
- Their thick cell walls are composed of the compounds cellulose and pectin.
- These cells are often found under the epidermis, or the outer layer of cells in young stems and in leaf veins.
Sclerenchyma:
- Sclerenchyma is the supporting tissue in plants.Two types of sclerenchyma cells exist: fibers andsclereids.
- Their cell walls consist of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin.
- Sclerenchyma cells are the principal supporting cells in plant tissues that have ceased elongation.
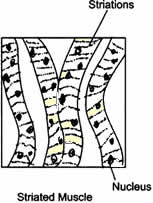
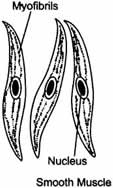
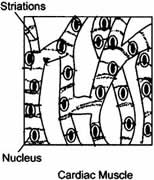
Question: With the help of diagram show the difference between striated muscle fibre, smooth muscle fibre and cardiac muscle fibre.
Answer:
Striated Muscle:
- The cells are long, cylindrical, unbranched and multinucleated.
- The cells show alternate light and dark bands.
Smooth Muscle:
- The cells are long with pointed ends, unbranched and uninucleated.
- The cell do not have such light and dark bands.
Cardiac Muscle:
- The cells are cylindrical, branched and uninucleated.
- The cells show alternate dark and light bands.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students