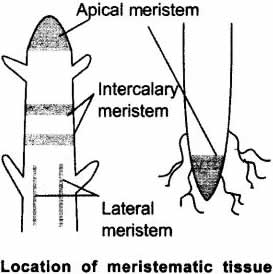
Question: Name different types of meristematic tissue and draw diagram to show their location.
Answer: The 3 different types of meristematic tissue are:
- Apical meristem—Function: growth in length.
- Lateral meristem—Function: growth in thickness.
- Intercalary meristem—Function: growth in intemodes.
Question: Explain the structure, function and location of nervous tissue.
Answer: Structure: Nervous tissue consists of cells called nerve cells joined end to end (neurons). A neuron (nerve cell) consists of a cell body with nucleus and cytoplasm. From these cell body a long thin hair-like parts arise called axon and many short branched parts called dendrites.
Location: Nervous tissue are present in brain, spinal cord and nerves. Function: Nervous tissue receives the stimuli and transmit the stimulus rapidly from one place to another within the body. The nerve impulse allows us to move our muscles and respond to any stimuli.
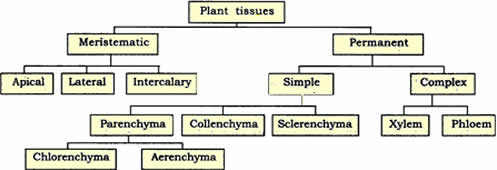
Question: Give the flow chart of plant tissues.
Answer:
Question: Write a note on plant tissues.
Answer: Plant tissues consist of two main types of tissue.
Meristematic tissue: The cells in this tissue divide very fast and helps in the growth of plants. Cells are round, oval, polygonal, no inter-cellular spaces. Present at tips of root, shoot, at nodes and the side of the stem.
Permanent tissue: The cells of meristematic tissue stops dividing, matures and forms permanent tissue. There are two types of permanent tissues.
- Simple tissue: All cells are same in structure and perform same function. Types of simple tissue are parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
- Complex tissue: It consists of group of different types of cells to perform same function. Types of complex tissue are xylem and phloem.
Parenchyma: Present in soft parts of the plant.
Collenchyma: Provides mechanical support to plant present in stalks. Sclerenchyma: They provide strength and flexibility to the plants.
Xylem: Conduct water in plants from root to shoot. Consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres.
Phloem: Conduct food to all parts of plant. Consist of sieve tubes, companion cell, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibers.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students