CBSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2024-25: Check and download the CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Syllabus for the new academic session 2024-2025. Go through the syllabus to know the latest course structure and examination pattern for CBSE Class 9 Maths.
CBSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2024-2025: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has released the syllabus for all Class 9 subjects. In this article, we have provided the detailed syllabus of CBSE Class 9 Maths subject to facilitate students’ preparation for the new academic session 2024-2025. This updated syllabus serves as a complete guide for the course structure, prescribed content and the criteria of assessment for Mathematics in class 9.
Understanding the syllabus is crucial at the onset of a new academic session. It helps students in the following ways:
- Curriculum Familiarization: It helps students become familiar with the subjects, topics, and chapters to be covered throughout the year.
- Goal Setting: Knowledge of the syllabus allows students to set academic goals and plan their studies effectively to achieve them.
- Time Management: Knowledge of prescribed weightage and amount of content allows students to allocate time to cover each topic systematically.
- Assessment Preparation: The syllabus provides students with an idea of the expected questions and topics for the examinations, allowing them to tailor their studies accordingly.
- Academic Performance: Being aware of the syllabus helps students track their progress and identify areas where they need improvement, leading to better academic performance.
Therefore, students must be familiar with the latest CBSE syllabus to excel and perform well in the CBSE Class 9 Mathematics exam in the upcoming academic year.
Note! The CBSE Class 9 Maths syllabus for the new academic session remains largely unchanged from the previous year. Notably, the same examination pattern continues without significant alterations. However, any modifications in the curriculum or assessment pattern throughout the academic year will be promptly updated here.
CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Syllabus 2024-2025
Check below the unit-wise weightage for CBSE Class 9 Maths:
CBSE Class 9 Maths Unit-Wise Weightage |
||
|
S. No.
|
Name of Unit
|
Marks
|
|
1.
|
NUMBER SYSTEMS
|
10
|
|
2.
|
ALGEBRA
|
20
|
|
3.
|
COORDINATE GEOMETRY
|
04
|
|
4.
|
GEOMETRY
|
27
|
|
5.
|
MENSURATION
|
13
|
|
6.
|
STATISTICS & PROBABILITY
|
06
|
|
|
TOTAL
|
80
|
CBSE Class 9 Maths Course Content
UNIT 1: NUMBER SYSTEMS
1. Real Numbers
1. Review of representation of natural numbers, integers, and rational numbers on the number line. Rational numbers as recurring/ terminating decimals. Operations on real numbers.
2. Examples of non-recurring/non-terminating decimals. Existence of non-rational numbers (irrational numbers) such as √2, √3 and their representation on the number line. Explaining that every real number is represented by a unique point on the number line and conversely, viz. every point on the number line represents a unique real number.
3. Definition of nth root of a real number.
4. Rationalization (with precise meaning) of real numbers of the type 1/(a+b√x) and 1/(√x + √y) (and their combinations) where x and y are natural number and a and b are integers.
5. Recall of laws of exponents with integral powers. Rational exponents with positive real bases (to be done by particular cases, allowing learner to arrive at the general laws.)
UNIT 2: ALGEBRA
1. Polynomials
Definition of a polynomial in one variable, with examples and counter examples. Coefficients of a polynomial, terms of a polynomial and zero polynomial. Degree of a polynomial. Constant, linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials. Monomials, binomials, trinomials. Factors and multiples. Zeros of a polynomial. Motivate and State the Remainder Theorem with examples. Statement and proof of the Factor Theorem. Factorization of ax2 + bx + c, a ≠ 0 where a, b and c are real numbers, and of cubic polynomials using the Factor Theorem. Recall of algebraic expressions and identities. Verification of identities:
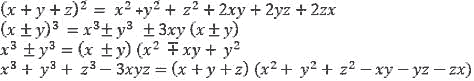
and their use in factorization of polynomials.
2. Linear Equations In Two Variables
Recall of linear equations in one variable. Introduction to the equation in two variables. Focus on linear equations of the type ax + by + c=0. Explain that a linear equation in two variables has infinitely many solutions and justify their being written as ordered pairs of real numbers, plotting them and showing that they lie on a line.
UNIT 3: COORDINATE GEOMETRY COORDINATE GEOMETRY
The Cartesian plane, coordinates of a point, names and terms associated with the coordinate plane, notations.
UNIT 4: GEOMETRY
1. Introduction To Euclid’S Geometry
History – Geometry in India and Euclid’s geometry. Euclid’s method of formalizing observed phenomenon into rigorous Mathematics with definitions, common/obvious notions, axioms/postulates and theorems. The five postulates of Euclid. Showing the relationship between axiom and theorem, for example: (Axiom)
1. Given two distinct points, there exists one and only one line through them. (Theorem)
2. (Prove) Two distinct lines cannot have more than one point in common.
2. Lines And Angles
1. (Motivate) If a ray stands on a line, then the sum of the two adjacent angles so formed is 180O and the converse.
2. (Prove) If two lines intersect, vertically opposite angles are equal.
3. (Motivate) Lines which are parallel to a given line are parallel.
3. Triangles
1. (Motivate) Two triangles are congruent if any two sides and the included angle of one triangle is equal to any two sides and the included angle of the other triangle (SAS Congruence).
2. (Prove) Two triangles are congruent if any two angles and the included side of one triangle is equal to any two angles and the included side of the other triangle (ASA Congruence).
3. (Motivate) Two triangles are congruent if the three sides of one triangle are equal to three sides of the other triangle (SSS Congruence).
4. (Motivate) Two right triangles are congruent if the hypotenuse and a side of one triangle are equal (respectively) to the hypotenuse and a side of the other triangle. (RHS Congruence)
5. (Prove) The angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal.
6. (Motivate) The sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are equal.
4. Quadrilaterals
1. (Prove) The diagonal divides a parallelogram into two congruent triangles.
2. (Motivate) In a parallelogram opposite sides are equal, and conversely.
3. (Motivate) In a parallelogram opposite angles are equal, and conversely.
4. (Motivate) A quadrilateral is a parallelogram if a pair of its opposite sides is parallel and equal.
5. (Motivate) In a parallelogram, the diagonals bisect each other and conversely.
6. (Motivate) In a triangle, the line segment joining the mid points of any two sides is parallel to the third side and in half of it and (motivate) its converse.
5. Circles
1. (Prove) Equal chords of a circle subtend equal angles at the center and (motivate) its converse.
2. (Motivate) The perpendicular from the center of a circle to a chord bisects the chord and conversely, the line drawn through the center of a circle to bisect a chord is perpendicular to the chord.
3. (Motivate) Equal chords of a circle (or of congruent circles) are equidistant from the center (or their respective centers) and conversely.
4. (Prove) The angle subtended by an arc at the center is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle.
5. (Motivate) Angles in the same segment of a circle are equal.
6. (Motivate) If a line segment joining two points subtends equal angle at two other points lying on the same side of the line containing the segment, the four points lie on a circle.
7. (Motivate) The sum of either of the pair of the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180° and its converse.
UNIT 5: MENSURATION
1. Areas
Area of a triangle using Heron’s formula (without proof)
2. Surface Areas And Volumes
Surface areas and volumes of spheres (including hemispheres) and right circular cones.
UNIT 6: STATISTICS & PROBABILITY
Statistics
Bar graphs, histograms (with varying base lengths), and frequency polygons.
Internal Assessment – 20 Marks
Internal assessment for mathematics in class 9 will be conducted based on the following criteria:
| Pen Paper Test and Multiple Assessment (5+5) | 10 Marks |
| Portfolio | 05 Marks |
| Lab Practical (Lab activities to be done from the prescribed books) | 05 Marks |
| Total | 20 Marks |
Prescribed Textbooks for CBSE Class 9 Maths
- Mathematics – Textbook for class IX – NCERT Publication
- Guidelines for Mathematics Laboratory in Schools, class IX – CBSE Publication
- Laboratory Manual – Mathematics, secondary stage – NCERT Publication
- Mathematics exemplar problems for class IX, NCERT publication.
CBSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2024-2025 PDF – Download
Download CBSE Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2024-25 in PDF
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students





