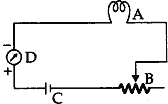Question: 400 J of heat is produced is 4 s in a 4 Ω resistor. Find potential difference across the resistor.
Answer: H = V²t/R
V = √RH/t
= √4×400/4
= 20 V
Question: A wire of resistivity ‘ρ’ is pulled to double its length. What will be its new resistivity?
Answer: Resistivity remains the same, i.e., ‘ρ’.
Question: What is meant by potential difference between two points?
Answer: Potential difference between two points in an electric field is the amount of work done to move a unit charge from one point to other.
Question: What is meant by saying that the potential difference between the two points is ‘1 V’ ?
Answer: It means that 1 J of work has been done in moving 1 coulomb of between the two points.
Question: The amount of charge passing through a cell in four second is 12 C. Find the current supplied by cell.
Answer: Charge, Q = 12 C, time t=4 s
∴ Current, I = Q/t = 12/4 = 3 A
Question: Calculate the number of electrons that would flow per second through the cross-section of a wire when 1 A current flows in it.
Answer: Here, I = 1 A, t = 1 s
∴ Q = I×t = 1 A × 1 s = 1 C
Number of electrons = 1C/1.6 ×10-19C
= 0.625 ×119
= 6.25 × 1018
Question: Name the device / instrument used to measure potential difference. How is it connected in electric circuit?
Answer: Voltmeter is used to measure potential difference. It is connected in parallel.
Question: What is the resistance of on ideal voltmeter?
Answer: A voltmeter has a very high resistance and for an ideal voltmeter, its value is infinity.
Question: List in a tabular form two differences between a voltmeter and an ammeter.
Answer: Voltmeter:
- Used to measure potential difference.
- Connected in parallel in an electric circuit.
- Has high resistance.
Ammeter:
- Used to measure current.
- Connected in series in the electric circuit.
- Has low resistance.
Question:
(a) What are the values of mA and µA?
(b) Draw the symbols of battery and rheostat.
Answer:
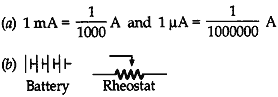
Question: Given below is a circuit showing current flowing in it. Identify each component A, B, C, D of this circuit.
Answer: A = Electric bulb, B = Rheostat, C = Electric cell, D = Ammeter
Question: State the factors on which the heat produced in a current carrying conductor depends. Give one practical application of this effect.
Answer:
- Heat produced in a current carrying conductor depends upon:
(i) Square of the current (I²).
(ii) Resistance of the given conductor (R).
(iii) Time for which the current flows (t). - This effect is applicable in electric heating device like electric iron.
Question: A large number of free electrons are present in metals yet no current flows in the absence of electric potential across it. Explain the statement with reason.
Answer: A large number of free electrons are present in metals, yet no current flows. It is because the electrons move only if there is a difference of electric pressure – called as the potential difference along the conductor. The potential difference sets the charges in motion in the conductor and produces an electric current.
Question: How much current will an electric bulb of resistance 1100 Ω draw from a 220 V source? If a heater of resistance 100 Ω is connected to the same source instead of the bulb, calculate the current drawn by the heater.
Answer: I = V/R = 1100/220 = 5 A
In case of heater, I = 1100/100 = 11A
Question: Out of the wire X and Y shown below which one has greater resistance. Justify your answer.
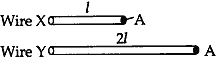
Answer: Wire Y has greater resistance because resistance is directly proportional to the length of the conductor.
Question:
-
Resistivity of iron is 10 × 10-8 Ω m and of mercury is 94 × 10-8 Ω m. Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor? Give reason.
-
Resistivity of a material A is in the range of 1010 – 10-8 Ω m. Which of the two will behave as an insulator and why?
Answer:
- Iron, because lower the resistivity, better is the conductor.
- Material A, because insulators have higher resistivity.
Question: Elements of electric toasters and electric iron are made of a alloy rather than a pure metal. Give two reasons to justify the statement.
Answer:
- Alloys do not oxidize readily at high temperature, so they are more resistant to corrosion.
- Alloys have lower electrical conductivity than pure metals.
Question: A thick wire and a thin wire of the same material are successively connected to the same circuit to find their respective resistance. Which one will have lower resistance? Give reason.
Answer: Thick wire will have lower resistance because resistivity is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section of the conductor.
Question: Mention two special features of the material to be used as element of an electric iron.
Answer: The material should have: (1) high resistivity and (2) high melting point.
Question: Given reason for the following:
-
Tungsten used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamp.
-
Why do we use copper and aluminium wires for transmission of electric current?
Answer:
- Tungsten is used in making the filament of an electric bulb because:
(i) Tungsten has high melting point.
(ii) Tungsten has high resistivity to retain much heat. - Copper and aluminium have low resistivity and they are good conductors of electricity. So, they are used for transmission of electric current.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students