Question: Describe double circulation in human beings. Why is it necessary?
Answer: The double circulatory system of blood flow refers to the separate systems of pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation.
The adult human heart consists of two separated pumps, the right side with the right atrium and ventricle which pumps deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary circulation.
The oxygenated blood re-enters the left side of the heart through the pulmonary vein into the left atrium and passes to the left ventricle where it is pumped to the rest of the body. This part of the circulation is called as systemic circulation. This type of circulation is called double circulation. The advantage of a double circulatory system is that blood can be pumped to the rest of the body at a higher pressure.
Question: What would be the consequences of a deficiency of hemoglobin in our bodies?
Answer: Hemoglobin is a red pigment present in our blood which carries oxygen to all the parts of the body.
If there is deficiency of hemoglobin then amount of oxygen reaching our body cells will decrease.
Which may lead to release of less energy in our body, leading to a disease called anemia.
Breathlessness, tiredness and weakness are the symptoms of anemia.
Question: What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem?
Answer: Transport in Xylem:
- Water and mineral salts are transported.
- The transport is generally passive.
- Vessels and tracheids are dead cells.
Transport in Phloem:
- Food in aqueous form is trans-located.
- The transport is active.
- Sieve tubes and companion cells are living cells.
Question: Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
Answer: Alveoli:
- It is the structural and functional unit of lungs.
- It is thin walled, has a large surface area and is richly supplied with blood vessels.
- It removes carbon dioxide from the blood.
Nephron:
- It is the structural and functional unit of kidneys.
- It is thin walled, has a large surface area and is richly supplied with blood vessels.
- It removes nitrogenous wastes from the blood.
Question:
- State reason for the following:
(i) Herbivores need a longer small intestine while carnivores have shorter small intestine.
(ii) The lings are designed in human beings to maximize the area for exchange of gases. - The rate of breathing in aquatic organisms is much faster than that seen in terrestrial organisms.
Answer:
- (i) Herbivores which eat grass have a longer small intestine for the digestion of cellulose because cellulose takes much time to be digested and it remains for a longer time inside the small intestine.
(ii) Carnivores which eat meat have a shorter small intestine because meat is easily digestible. Hence, they does not need a longer smaller intestine. - (i) Inside the lungs, trachea divides and redivides to form numerous fine tubes, the bronchi and bronchioles which finally end in inflated balloon like structures called alveoli. Alveoli have extensive network of blood vessels in their thin walls. Hence provide large surface area for diffusion of gases across their walls.
(ii) The amount of dissolved oxygen is fairly low as compared to oxygen in the air. The fishes take in water through their mouths and force it past the gills where the dissolved oxygen is taken up by blood.
Question: (1). Discuss the role of HCl, pepsin, bile and trypsin in the digestion of food in human beings.
(2). Where are gastric gland located in alimentary canal of human?
Answer:
- HCl: It creates an acidic medium which facilitates the action of pepsin.
Pepsin: It digest proteins into peptones.
Bile: Bile breaks down fats into fat globules.
Trypsin: Trypsin digest protein. - Gastric glands are present in the wall of the stomach.
Question:
- Bile doesn’t contain any digestive enzyme, yet it is important for digestion of food. Why?
- Name the products formed after complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats in small intestine.
Answer:
- Bile make the acidic food coming from stomach alkaline which enables pancreatic enzymes to act. Bile salts break the large fat globules into smaller globules due to which efficiency of enzyme action increases.
- Carbohydrates: Glucose
Proteins: Amino acids
Fats: Fatty acids and glycerol
Question:
- Draw a sectional view of the human heart and label on it Aorta, Pulmonary arteries, Vena cava, Left ventricle.
- Why is double circulation of blood necessary in human beings?
Answer:
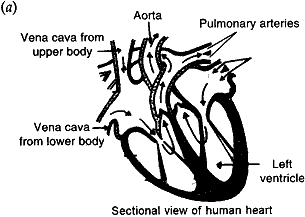
(b) Double circulation of blood is necessary to:
- Separate deoxygenated blood from oxygenated blood.
- Meet high energy and oxygen demands.
- Maintain constant body temperature.
Question:
- Draw a diagram of the human system and label in it:
(i) Kidney
(ii) Ureter
(iii) Urinary bladder
(iv) Urethra - Name the two major components of normal human urine.
Answer:
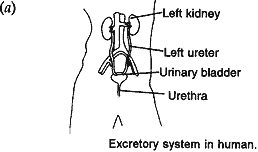
(b) The two major components of human urine are water and nitrogenous substances, most of which is urea.
Question:
- Draw a diagram of human alimentary canal and label on it: Oesophagus, Gall bladder, Liver and Pancreas.
- Explain the statement, ‘Bile does not contain any enzyme but it is essential for digestion’.
Answer:
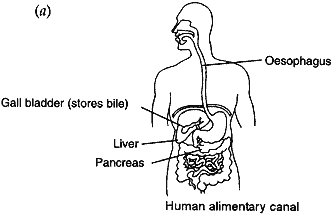
(b) Bile does not contain any enzyme but it is essential for digestion because:
- It maintains alkaline medium for other enzyme to work.
- It helps in emulsification of fats i.e., converts them into small globules.
Question:
- Draw a diagram of excretory system in human beings and label on it: Aorta, Vena cava, Urinary bladder, Urethra.
- List two vital functions of the kidney.
Answer:
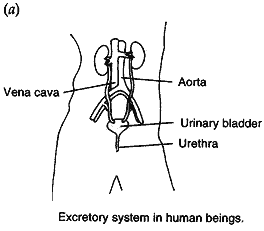
(b) Two vital functions of kidneys are:
- They maintain the pH and salt concentration of body constant and also the water balance.
- They help in removal of waste products that are harmful for human body.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students