Question: What is the nature of magnetic field produced by a current carrying circular coil? Explain with the help of an experiment.
Answer: Bend a copper wire in a circular shape. Pass the coil through a cardboard. Connect the free ends of the coil to a battery and a key. Sprinkle some iron filings on the cardboard. Put on the key you will find that the iron filings arrange themselves in the form of concentric circles. The magnetic lines of force near each segment of wire are circular and form concentric circles. Where as the lines of force near the centre of the coil are almost straight lines. Note that at the center of the coil, the magnetic field is uniform and perpendicular to the plane of the coil.
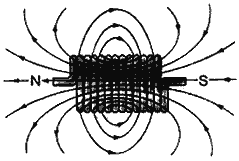
Question: What is a solenoid? Explain with the help of a figure how a solenoid behaves like a bar magnet.
Answer: A solenoid is a cylindrical coil of many tightly wound turns of insulated wires with generally wound turns of insulated wires with generally diameter of the coil smaller than its length. When a current is passed through a solenoid, a magnetic field is developed in it. As the electric current in each circular coil flows in the same direction, the magnetic field of the loop makes one end of a solenoid act as a North pole of a bar magnet and the other end as the South pole. The figure is as shown below:
Question: What are the factors on which the magnetic field due to a current carrying solenoid depends?
Answer: The strength of magnetic field produced by a current carrying solenoids depends on the following factors:
- Directly on the number of turns in the coil.
- Directly on the strength of the current.
- Nature of the core material. When a soft iron core is used as a core material, a very strong magnetic field is produced.
Question: Why does a magnetic needle deflect when brought close to a current carrying conductor? Explain the rule to find the direction of force on a current carrying conductor.
Answer: When a magnetic needle is brought near a current carrying conductor, the needle gets deflected, i.e., the magnetic field of the current carrying conductor exerts a force on the magnetic needle.
The direction of force experienced by a current carrying conductor an be found by Fleming’s left hand rule which states that stretch out the forefinger, middle finger and the thumb perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger gives the direction of the magnetic field, the middle finger gives the direction of current, then the thumb will give the direction of the force experienced by the current carrying conductor.
Question: State Faraday’s Laws of electromagnetic induction.
Answer: Faraday put forward the following laws called Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction.
- Whenever the magnetic field (flux) linked with a coil changes, an induced emf is produced.
- The induced emf lasts as long as the change in magnetic field (flux) continues.
- The induced emf in the closed loop equals the negative rate of change of magnetic field (flux) through the loop.
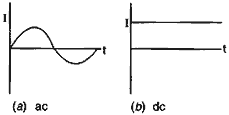
Question: Differentiate between ac and dc along with the graph.
Answer: The electric current which changes its direction (or polarity) after certain fixed interval of time is called ac or alternating current. Thus, in ac, the polarity (+ or -) is not fixed and its current v/s time graph will be shown in figure (a).
The electric current which always flows in the same direction is called direct current or dc. Thus, in dc the polarisation (+ or -) are fixed. The current obtained from the battery or a cell is dc. The current v/s time graph of dc is as shown is figure (b)
Question: What is a fuse? How does it function?
Answer: An electric fuse is a device which is used to limit the current in an electric circuit. The use of fuse is so safeguard the circuit and the appliances connected to it from damaged. The fuse is a short piece of wire made of a material having a low melting point. When electric current is passed through it the fuse gets heated. If the current passing through the fuse exceeds the safe guard limit the heat produced melts the fuse and this breaks the circuit.
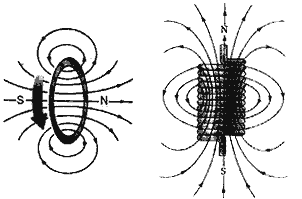
Question: Draw a rough sketch of the pattern of the field lines due to:
(i) Current flowing into a circular coil and
(ii) Solenoid carrying current.
Answer: The sketches are shown below:
Question: Describe an experiment to illustrate the action of an electric fuse.
Answer: Take a thin strip of aluminium foil about 3 to 5 cm in length. Fix its two ends on the tips of two iron nails placed vertically on the table. Now, connect the ends of the two nails to the two terminals of a thorough the nails and the foil. Also, connect a bulb in the circuit. As the current flows through the circuit the foil gets heated-up and eventually burns out thereby breaking the circuit.
Question: What is the nature of magnetic field produced by a current flowing in a straight conductor? Name the rule used to find the direction of the magnetic field.
Answer: When current flows through a straight conductor the magnetic field is circular i.e., the magnetic field lines are in the form of concentric circles with the conductor at the centre. The direction of magnetic field is obtained by using Right hand thumb rule.
Question: On what factors does the force experienced by a current carrying conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field depend?
Answer: The force depends upon the following factors:
- The strength of the magnetic field.
- The strength of the electric current.
- The length of the conductor.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students