Question: A coil made of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen to the deflection of the galvanometer if this coil is moved towards a stationary bar magnet and then moved away from it? Give reason for your answer and name the phenomenon involved.
Answer: When coil is moved towards a stationary magnet, the magnetic field associated with the coil will change and so current will be induced in the coil. This causes the galvanometer to show deflection in one direction. Now, when coil is moved away, the magnetic field will decrease and so current induces in the opposite direction causing galvanometer to show opposite deflection. The phenomenon is electromagnetic induction.
Question: What is meant by overloading of an electrical circuit? Explain two possible causes due to which overloading may occur in household circuit. Explain one precaution that should be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuit.
Answer: It is a situation in a circuit when current increases abruptly.
- Accidental hike in the supply voltage.
- Too many appliances connected to a single socket.
Too many devices should not be connected to the same socket.
Question: Write one difference between direct current and alternating current. Which one of the two is mostly produced at power stations in our country? Name one device which provides alternating current. State one important advantage of using alternating current.
Answer: Direct current does not change its direction with time whereas alternating current reverses its direction periodically. Most power stations produce ac in India. An ac generator produces alternating current. Electric power can be transmitted over long distances without much loss of energy.
Question: Define magnetic field. A compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet. Why? List three properties of magnetic field lines.
Answer: Magnetic field is the region around a magnet where its magnetic force can be experienced.
A compass needle gets deflected due to the force acting on its poles due to the magnetic field of the bar magnet.
Properties of magnetic field:
- The direction of magnetic field lines is from north pole to south pole.
- They are closed curves.
- No two magnetic field lines intersect.
Question: State one main difference between ac and dc. Why ac is preferred over dc for long range transmission of electric power? Name one source each of dc and ac.
Answer: The dc always flows in one direction while ac reverses its direction periodically.
This is because in case of a electric power can be transmitted over long distances without much loss of energy.
Source of ac – ac generator.
Source of dc – dc generator/cell.
Question: (1). Mention the colour code used for live, neutral and earth wire.
(2). You want to connect a 2 kW electric oven in the electric circuit. In which power line would you connect it wrongly in the other power line?
Answer:
- Rad, Black, Green.
- 15 A, as it draws a large current. If it is connected to other power line, the fuse will blow off.
Question: Explain the meaning of the word “electromagnetic” and “induction” in the term electromagnetic induction. List three factors on which the value of induced current produced in a circuit depends. Name and state the rule used to determine the direction of induced current. State one practical application of this phenomenon in everyday life.
Answer: Electromagnetic means production of electric current in a coil under the influence of magnetic field and Induction means bringing about an electrical flow in the coil without coming in contact with a magnetised body.
Factors: (i) Number of turns in the coil.
(ii) Strength of the magnet.
(iii) Speed of the magnet.
Fleming’s right hand rule: Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of right hand so that they are perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger indicates the direction of the magnetic field and the thumb shows the direction of motion of the conductor, then the middle finger will show the direction of induced current.
Application: Generator.
Question: (a) Draw magnetic field lines of a bar magnet. “Two magnetic field lines never intersect each other”. Why?
(b). An electric oven of 1.5 kW is operated in a domestic circuit (220 V) that has a current rating of 5 A. What result do you expect in this case? Explain.
Answer: (a) Magnetic field lines around a bar magnet.
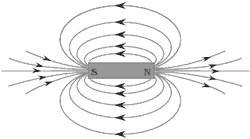
If two magnetic field lines intersect at a point, then at the point of intersection, there must be two directions of the same field, which is not possible.
(b) Here, P = 1.5 kW = 1500 W
∴ Current I = P/V = 1500/220 = 7 A
Thus, the current flowing through the circuit when oven is ON is nearly 7 A which is higher than the current rating (5 A) of the circuit.
∴ The wiring of the circuit may burn, fuse wire will also blow of breaking the circuit and stopping the current supply.
Question: (1). Explain any three properties of magnetic field lines.
(2). Give two uses of magnetic compass.
Answer:
- (i) Field lines emerge from north pole and merge at south pole outside the magnet.
(ii) They are closed curves.
(iii) Magnetic force is greater where the field lines are crowded
(iv) No two field lines are found to cross each other. - Uses of magnetic compass:
(i) A magnetic compass can be used to find direction.
(ii) It can be used to test if a substance has magnetic properties.
Question: What is an electromagnet? What decides its polarity? How it differs from a permanents magnet? List the three factors and explain how strength of an electromagnet depends on these.
Answer:
- When a soft iron is placed inside a solenoid and current is passed through it, then the soft iron gets magnetised. The magnet so formed is called an electromagnet.
- Its polarity is decided by the direction of current flowing through the solenoid.
- Permanent magnets have constant magnetic field around them whereas magnetic field of electromagnet is temporary.
- Strength of an electromagnet depends on:
(i) The number of turns in the solenoid.
(ii) Strength of current flowing through the solenoid.
(iii) Position of soft iron core within the solenoid.
Question: (1). An electric current is passed in a horizontal copper wire from east to west. Explain your observations when a compass needle is placed (i) below this wire, (ii) above the wire. Draw inference from your observations.
(2). List the factors on which the strength of the magnetic field due to a straight conductor carrying current depend. How should these be changed to decreases magnetic field at a point?
Answer:
- In both the cases, the direction of the compass needle will remain the same.
- (i) (a) The strength of the current.
(b) Distance of the point from the conductor.
(ii). By decreasing the strength of the current, magnetic field at the point can be decreased.
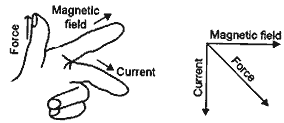
Question: (1). Name two electrical appliances of daily use in which electric motor is used.
(2). Name and state the principle on which an electric motor works.
Answer:
- Electric motor is commonly used in fan, washing machine, mixer, etc.
- An electric motor works on the Fleming’s left hand rule.
Fleming’s left hand rule: When we stretch our thumb, forefinger and middle finger so that they mutually perpendicular to one another, the forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field and the middle of the magnetic field and the middle finger points in the direction of the current; the thumb gives the direction of the force acting on the conductor.
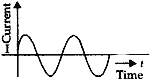
Question: (a). Write three differences between ac and dc.
(b). State the frequency of ac supply inn India and mention the potential difference between neutral and live wire in domestic circuit.
How many times does ac change its direction in one second?
Answer: (a)
ac:
- It can be transmitted over long distance effectively.
- It changes its direction at regular interval of time.
- It is represented by:
dc:
- It cannot be transmitted over long distance effectively.
- It does not change direction.
- It is represented by:
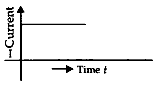
(b) * 50 Hz
*240 V
* 100 times
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students