10th Class CBSE SST Board Exam 2025: February 2025 – time duration 03 hours with maximum marks 80.
Note:
(1) Please check that this question paper contains 21 printed pages + 1 Map.
(2) Please check that this question paper contains 37 questions.
(3) Q.P. Code given on the right hand side of the question paper should be written on the title page of the answer-book by the candidate.
(4) Please write down the Serial Number of the question in the answer-book at the given place before attempting it.
(5) 15 minutes of time has been allotted to read this question paper. The question paper will be distributed at 10.15 am. From 10.15 a.m. to 10.30 a.m., the students will read the question paper only and will not write any answer on the answer-book during this period.
| School Name: | New Delhi 110085 India |
| Class: | 10th Standard (CBSE) |
| Subject: | Social Science Standard |
| Time Duration: | 03 Hours |
| Maximum Marks: | 80 |
| Date: | 25 February, 2025 |
General Instructions: Read the following instructions carefully and follow them:
1. This question paper contains 37 questions. All questions are compulsory.
2. Question paper is divided into SIX sections — Section A, B, C, D, E and F.
3. Section A — question number 1 to 20 are multiple choice type questions. Each question carries a 1 mark.
4. Section B — question number 21 to 24 are Very Short Answer type questions. Each question carries 2 marks. Answers to these questions should not exceed words.
5. Section C — question number 25 to 29 are Short Answer type questions. Each question carries 3 marks. Answer to these questions should not exceed 60 words:
6. Section D — question number 30 to 33 are Long Answer (LA) type questions. Each question carries 5 marks. Answers to these questions should not exceed 120 words.
7. Section E — question number 34 to 36 are Case-based / Source-based questions with three sub-questions. Each question carries 4 marks.
8 In Section F — question number 37 is a Map skill based question with two parts- (i) History (2 marks) and (ii) Geography (3 marks). This question carries a total of 5 marks.
9. In addition to this, NOTE that a separate question has been provided for the Visually Impaired Candidates in lieu of questions having visual inputs, Map etc. Such questions are to be attempted by the Visually Impaired Candidates only.
Section A:
Multiple Choice Questions (20 x 1 = 20)
Question 01. Why was the silk route considered a good example of vibrant pre-modern trade? Choose the most appropriate option from the following:
(a) Due to movement of silk cargoes
(b) Due to flow of silver and gold
(c) Due to linkage of China with Australia
(d) Due to trade and cultural exchange
Question 02. How did the British East India Company use Print Culture to promote its interests in India? Choose the correct option from the following:
(a) By censoring the Indian newspapers
(b) By funding the regional language newspapers
(c) By encouraging the development of independent Press
(d) By using print media to spread eastern culture
Question 03. Look at the given picture and identify the name of the painter of this painting from the following options:

(a) Rabindranath Tagore
(b) Abanindranath Tagore
(c) Debindranath Tagore
(d) Satyendranath Tagore
Note: The following question is for the Visually Impaired Candidates only in lieu of Q. No. 3.
Who amongst the following organized the ‘Depressed Class Association in 1930?
(a) B.L. Yadav
(b) C.R. Das
(c) M.R. Jayeker
(d) B.R. Ambedkar
Question 04. Arrange the following events in the chronological order and choose the correct option : 1
I. The Treaty of Vienna
II. The beginning of the Napoleonic wars
Il. Proclamation of the Prussian King William I as German Emperor
IV. Proclamation of Victor Emmanuel II as the King of Italy
Options:
(a) I, II, IV and II
(b) II, IV, I and III
(c) II, I, IV and III
(d) II, IIl, IV and I
Question 05. A researcher is examining a soil type which is formed by the weathering of volcanic rock and is rich in minerals. Which one of the following soils is it?
(a) Laterite soil
(b) Alluvial soil
(c) Black soil
(d) Desert soil
Question 06. Identify the crop with the help of information given in the box.
i. This crop is a major cash crop in India.
ii. It is cultivated mainly in the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
iii. It is known for its aroma.
Options:
(a) Tea
(b) Coffees
(c) Jute
(d) Cotton
Question 07. Match Column-I with Column-II and choose the correct option :
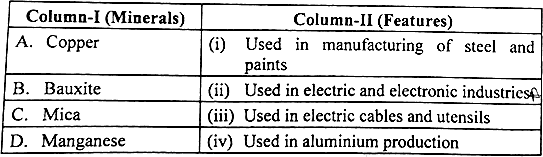
Options:
Question 08. Two statements are given below. They are Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Read both the statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A): The French speaking community was rich in comparison to the Dutch speaking community in Belgium.
Reason (R): The Dutch speaking community got the benefit of economic development and education much later.
Options:
(a) Both, (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both, (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is incorrect.
(d) (A) is incorrect but (R) is correct.
Question 09. How does the Indian federal structure promote balanced governance across the nation? Choose the most suitable option from the following:
(a) By allowing states to exercise complete autonomy on all issues
(b) By ensuring a division of power between centre and states
(c) By allowing all decision making processes under the Union Government.
(d) By giving more powers to local governments in comparison to slates.
Question 10. Which of the following is an example of horizontal power sharing in Indian democracy?
(a) Division of power between Central and State Governments.
(b) Division of power between Rural and Urban Governments.
(c) Division of power among Administration, Judiciary and Army.
(d) Division of power among Legislative, Executive and Judiciary.
Question 11. Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched ? 1
List-I (Regional Parties) List-II (Regions)
(a) Rashtriya Janta Dal — Uttar Pradesh
(b) Janta Dal (Secular) — Bihar
(c) Rashtriya Lok Dal — Assam
(d) Biju Janta Dal — Odisha
Question 12. In a democratic country the government adopts environment friendly policies with the help of citizens and experts. Which one of the following is a positive outcome of this process ? 1
(a) The government is capable of determining policies on its own.
(b) Citizens feel empowered to determine policies
(c) Corporates protect their own interest in determining policies.
(d) Market forces also influence the government for their interests.
Question 13. In which year the Constitution amendment providing for 33% representation of women in the local self governance system in India was made ? Choose the correct option: 1
(a) 1990
(b) 1984
(c) 1992
(d) 1988
Question 14. Read the table given below carefully and answer the question that follow:
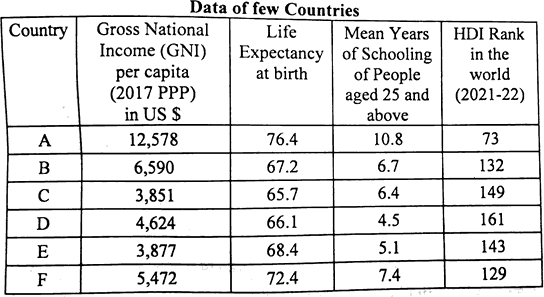
Which of the following countries has high per capita income, life expectancy at birth and high rank in human development index?
(a) A
(b) C
(c) E
(d) F
Question 15. The World Bank’s development report is prepared on the basis of which of the following:
(a) Per Capita Income
(b) Health Services
(c) Literacy
(d) Freedom
Question 16. Choose the odd one out from the following options regarding the sectors of economy:
(a) Pilot, Driver, Gardener
(b) Fisherman, Teacher, Lawyer
(c) Engineer, Professor, Farmers
(d) Doctor, Teacher, Lawyer
Question 17. Choose the correct option to fill the blank:
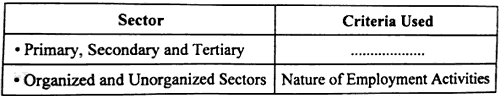
Options:
(a) Nature of social activities
(b) Nature of political activities
(c) Nature of production activities
(d) Nature of government activities
Question 18. Read the following sources of loan carefully and choose the correct option related to formal sources of credit. 1
(i) Commercial Bank
(ii) Landlords
(iii) Government
(iv) Money Lender
Options:
(a) (i) and (iii) are correct.
(b) (ii) and (iv) are correct.
(c) (i) and (ii) are correct.
(d) (ii) and (ii1) are correct.
Question 19. The growth of digital technology has greatly influenced globalization. Which of the following is its main benefit?
(a) Increased Communication Cost
(b) Limited Access to Information
(c) Enhanced Connectivity
(d) Slower Transaction Speed
Question 20. Read the following developmental goals and choose correct option of goals related to a student studying in university. 1
(i) Good opportunities for research.
(ii) Opportunities to pursue higher education abroad.
(iii) Opportunities for independence.
(iv) Opportunities for good employment.
Options:
(a) Only (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct.
(b) Only (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct.
(c) Only (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct.
(d) Only (i), (iii) and (iv) are correct.
Section B:
Very Short Answer Type Questions (4 x 2 = 8)
Question 21. Why was the Indian subcontinent significant to trade networks before European intervention? Explain.
Question 22. Suggest any two ways to increase women’s representation in leadership roles.
Question 23. (A) “Planning is the widely accepted strategy for judicious use of resources.” Explain the statement.
OR
(B) “An equitable distribution of resources has become essential for a sustained quality of human life.” Explain the statement.
Question 24. Explain the role of public facilities for quality of life.
Section C:
Short Answer Type Questions (5 x 3 = 15)
Question 25. (A) Describe the steps taken by French revolutionaries to create a sense of national unity and belonging. 3
OR
(B) Describe the historical factors that contributed to the emergence of nationalist tensions in the Balkans.
Question 26. Examine the measures taken by the government to make agriculture profitable in India.
Question 27. How did the trade policy implemented in 1991 stimulate globalization in India? Explain with example.
Question 28. Describe any three features of the Multi Party System.
Question 29.Analyse the significance of the Primary Sector in the Indian economy.
Section D:
Long Answer Type Questions (4 x 5 = 20)
Question 30. (A) Explain with examples the significance of the Non-cooperation Movement in the Indian national movement.
OR
(B) How did the Civil Disobedience Movement become a mass movement? Explain with examples.
Question 31. (A) “It would be beneficial to develop a sustainable way to meet the growing energy demand in India.” Support the statement by giving suitable arguments.
OR
(B) “We have to use a planned and sustainable manner to conserve our minerals.” Support the statement by giving suitable arguments.
Question 32. (A) “Democratic governance is responsive to the expectations of citizens.” Justify the statement with suitable arguments.
OR
(B) “Democracy accommodates social diversity better than dictatorship.” Justify the statement with suitable arguments.
Question 33. (A) Imagine you are a part of a ‘Self Help Group’’ (SHG). Explain the working system of the Self Help Group (SHG) to the new member.
OR
(B) Imagine that you are the Village Development Officer of a village. Explain the usefulness of formal sources of credit for the farmers.
Section E:
Case-based / Source-based Questions (3 x 4 = 12)
Question 34. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
New Forms of Publication
By the end of the nineteenth century, a new visual culture was taking shape. With the setting up of an increasing number of printing presses, visual images could be easily reproduced in multiple copies. Painters like Raja Ravi Varma produced images for mass circulation. Poor wood engravers who made woodblocks set up shop near the letterpresses, and were employed by print shops. Cheap prints and calendars, easily available in the bazaar, could be bought even by the poor to decorate the walls of their homes or places of work. These prints began shaping popular ideas about modernity and tradition, religion and politics, and society and culture. By the 1870s, caricatures and cartoons were being published in journals and newspapers, commenting on social and political issues. Some caricatures ridiculed the educated Indians’ fascination with Western tastes and clothes, while others expressed the fear of social change. There were imperial caricatures lampooning nationalists, as well as nationalist cartoons criticising imperial rule.
34.1 How did the development of printing technology impact visual culture?
34.2 How did Raja Ravi Varma contribute to the mass circulation of art India?
34.3 How did visual culture shape the memory of the 19% century social landscape? Explain.
Question 35. Read the given source and answer the questions that follow:
Sacred Groves — a wealth of diverse and rare species ‘ Nature worship is an age-old tribal belief based on the premise that all creations of nature have to be protected. Such beliefs have preserved several virgin forests in pristine form called Sacred Groves (the forests of God and Goddesses). These patches of forest or parts of large forests have been left untouched by the local people and any interference with them is banned.
Certain societies revere a particular tree which they have preserved from time immemorial. The Mundas and the Santhal of Chota Nagpur region worship mahua (Bassia latifolia) and kadamba (Anthocaphalus cadamba) trees, and the tribals of Odisha and Bihar worship the tamarind (Tamarindus indica) and mango (Mangifera indica) trees during weddings. To many of us, peepal and banyan trees are considered sacred.
Indian society comprises several cultures, each with its own set of traditional methods of conserving nature and its creations. Sacred qualities are often ascribed to springs, mountain peaks, plants and animals which are closely protected. You will find troops of macaques and langurs around many temples. They are fed daily and treated as a part of temple devotees. In and around Bishnoi villages in Rajasthan, herds of blackbuck (chinkara), nilgai and peacocks can be seen as an integral part of the community and nobody harms them.
35.1 How do sacred groves show the inter-connectivity of spirituality and ecology?
35.2 How do tribal practices promote conservation of forests?
35.4 Why is conservation of wildlife important for all of us? Explain.
Question 36. Read the following source and answer the questions that follow:
Local Self Government
The local government structure goes right up to the district level. A few gram panchayats are grouped together to form what is usually called a panchayat samiti or block or mandal. The members of this representative body are elected by all the panchayat members in that area. All the panchayat samitis or mandals in a district together constitute the zilla (district) parishad. Most members of the zilla parishad are elected. Members of the Lok Sabha and MLAs of that district and some other officials of other district level bodies are also its members. Zilla parishad chairperson is the political head of the Zilla parishad.
Similarly, local government bodies exist for urban areas as well. Municipalities are set up in towns. Big cities are constituted into municipal corporations. Both municipalities and municipal corporations are controlled by elected bodies consisting of people’s representatives. Municipal chairperson is the political head of the municipality. In a municipal corporation, such an officer is called the mayor. This new system of local governance is the largest experiment inducted anywhere in the world.
36.1 Explain the relationship between gram panchayats and panchayat samitis?
36.2 How is the structure of a municipal corporation different from a municipality?
36.3 How does the local government structure promote democracy? Examine.
Section F:
Map Skill Based Questions (2 x 3 = 6)
Question 37. (i) Two places (A) and (B) have been marked on the given political outline map of India. Identify them with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them:
(a) The place Where the Session of Indian National Congress was held in 1927.
(b) The place where Gandhiji broke the Salt Law.
Note: The following questions are for the Visually Impaired Candidates only in lieu of Q. No. 37(i).
(a) Name the place where the Session of Indian National Congress was held in 1927.
(b) Name the place where Gandhiji broke the Salt Law.
Question 37. (ii) On the same political outline map of India, locate and label any three of the following with suitable symbols:
(a) A major dam on the Chenab river
(b) Nuclear Power Plant located in Uttar Pradesh
(c) A major Software Technology Park located in Karnataka
(d) A major Sea Port located in Odisha
Note: The following questions are for the Visually Impaired Candidates only in lieu of Q. No. 37(ii).
Attempt any three questions:
(a) Name the place where the major dam is located on the Chenab river.
(b) Name the place where Nuclear Power Plant is located in Uttar Pradesh.
(c) Name the place where a major Software Technology Park is located in Karnataka.
(d) Name the place where a major Sea Port is located in Odisha.
 Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students
Class Notes NCERT Solutions for CBSE Students





